Published online by Cambridge University Press: 25 October 2019
We study rotating homogeneous turbulent convection forced by a mean vertical temperature gradient by means of direct numerical simulations in the Boussinesq approximation in a rotating frame. In the absence of rotation, our results are in agreement with the ‘ultimate regime of thermal convection’ for the scaling of the Nusselt and Reynolds numbers versus Rayleigh and Prandtl numbers. Rotation is found to increase both 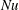 $Nu$ and
$Nu$ and 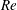 $Re$ at fixed
$Re$ at fixed 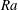 $Ra$ with a maximum enhancement for intermediate values of the Rossby numbers, qualitatively similar, but with stronger intensity, to what is observed in Rayleigh–Bénard rotating convection. Our results are interpreted in terms of a quasi-bidimensionalization of the flow with the formation of columnar structures displaying strong correlation between the temperature and the vertical velocity fields.
$Ra$ with a maximum enhancement for intermediate values of the Rossby numbers, qualitatively similar, but with stronger intensity, to what is observed in Rayleigh–Bénard rotating convection. Our results are interpreted in terms of a quasi-bidimensionalization of the flow with the formation of columnar structures displaying strong correlation between the temperature and the vertical velocity fields.