Article contents
Polarized vortex reconnection
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 12 July 2021
Abstract
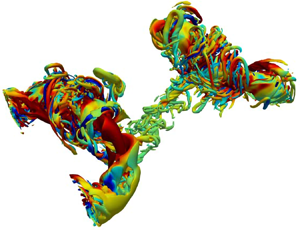
Polarized vortical structures (i.e. with axial flow, thus coiled vortex lines) are generic to turbulent flows – hence the importance of their dynamics, interactions and cascade. Direct numerical simulations of two anti-parallel polarized vortex tubes are performed for vortex Reynolds numbers  $Re$ (
$Re$ ( $\equiv \varGamma /\nu$) up to
$\equiv \varGamma /\nu$) up to  $9000$ and initial polarization strength
$9000$ and initial polarization strength  $q$ (ratio of peak axial to azimuthal velocities) between
$q$ (ratio of peak axial to azimuthal velocities) between  $0$ and
$0$ and  $4/3$. For both counter- and co-polarized cases, although the reconnection is delayed as
$4/3$. For both counter- and co-polarized cases, although the reconnection is delayed as  $q$ increases – mainly due to weakened self-induction – it is more rapid and more complete for small
$q$ increases – mainly due to weakened self-induction – it is more rapid and more complete for small  $q$. Enstrophy growth and energy cascade are suppressed for weak polarization (
$q$. Enstrophy growth and energy cascade are suppressed for weak polarization ( $q < 1/2$) due to depleted nonlinearity, but are enhanced for strong polarization (
$q < 1/2$) due to depleted nonlinearity, but are enhanced for strong polarization ( $q > 1/2$) due to instability and/or transient growth. When counter-polarized, numerous structures with both positive and negative helicity densities (i.e.
$q > 1/2$) due to instability and/or transient growth. When counter-polarized, numerous structures with both positive and negative helicity densities (i.e.  $\pm h$) are generated. For large
$\pm h$) are generated. For large  $q$, strong axial flows opposite to the initial flows occur – causing polarization reversals. For the co-polarized cases, although
$q$, strong axial flows opposite to the initial flows occur – causing polarization reversals. For the co-polarized cases, although  $+h$ predominates,
$+h$ predominates,  $-h$ structures also form and interact with positive ones – leading to helicity cascade to small scales. As
$-h$ structures also form and interact with positive ones – leading to helicity cascade to small scales. As  $Re$ increases, small scales are more numerous: for counter-polarized cases, the threads undergo successive reconnections in a cascade – akin to the unpolarized case; for co-polarized cases, the newly formed vortex ring breaks up with numerous hairpin vortices wrapping around it. Increasing
$Re$ increases, small scales are more numerous: for counter-polarized cases, the threads undergo successive reconnections in a cascade – akin to the unpolarized case; for co-polarized cases, the newly formed vortex ring breaks up with numerous hairpin vortices wrapping around it. Increasing  $q$ alters the energy spectrum in the inertial range with a scaling varying from
$q$ alters the energy spectrum in the inertial range with a scaling varying from  $k^{-5/3}$ for the unpolarized case to
$k^{-5/3}$ for the unpolarized case to  $k^{-7/3}$ for the strongly polarized case, which seems to be associated with the enhanced vortex spiralling. In addition, for the strongly co-polarized cases, a
$k^{-7/3}$ for the strongly polarized case, which seems to be associated with the enhanced vortex spiralling. In addition, for the strongly co-polarized cases, a  $k^{-4/3}$ helicity spectrum develops. Furthermore, most of the energy and helicity in the inertial range with scale
$k^{-4/3}$ helicity spectrum develops. Furthermore, most of the energy and helicity in the inertial range with scale  $L$ transfer to scales between
$L$ transfer to scales between  $0.3L$ and
$0.3L$ and  $0.4L$. Therefore, polarization can significantly alter the dynamics of vortex reconnection as well as turbulence cascade.
$0.4L$. Therefore, polarization can significantly alter the dynamics of vortex reconnection as well as turbulence cascade.
JFM classification
Information
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2021. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
REFERENCES
Yao and Hussain supplementary movie 1
Isosurface of vorticity magnitude shaded with contours of axial vorticity for counter-polarized cases at Re=5000.
Yao and Hussain supplementary movie 2
Isosurface of vorticity magnitude shaded with contours of axial vorticity for co-polarized cases at Re=5000.
- 8
- Cited by


