Published online by Cambridge University Press: 06 April 2021
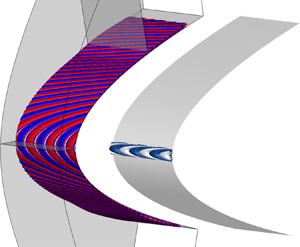
This study performs global stability/receptivity analyses of hypersonic flows over a swept blunt body with infinite span. For the first time, we obtain the characteristics of the leading attachment-line mode to the variation of sweep angles from  $20^{\circ }$ to
$20^{\circ }$ to  $70^{\circ }$. The global eigenfunctions exhibit the characteristics of the attachment-line instability at the leading edge. At the same time, cross-flow (at small sweep angles) or second Mack mode (at larger sweep angles) dominates further downstream. We establish an adjoint-based bi-orthogonal eigenfunction system to address the receptivity problem of such flows to any external forces and boundary perturbations. The receptivity analyses indicate that the global modes are the most responsive to external forces and surface perturbations applied in the vicinity of the attachment line, regardless of the sweep angles. It is also proven that the present global extension of the bi-orthogonal eigenfunction system can be successfully applied to complex hypersonic flows.
$70^{\circ }$. The global eigenfunctions exhibit the characteristics of the attachment-line instability at the leading edge. At the same time, cross-flow (at small sweep angles) or second Mack mode (at larger sweep angles) dominates further downstream. We establish an adjoint-based bi-orthogonal eigenfunction system to address the receptivity problem of such flows to any external forces and boundary perturbations. The receptivity analyses indicate that the global modes are the most responsive to external forces and surface perturbations applied in the vicinity of the attachment line, regardless of the sweep angles. It is also proven that the present global extension of the bi-orthogonal eigenfunction system can be successfully applied to complex hypersonic flows.