No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Streaming and diffusion in the cochlea
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 16 July 2025
Abstract
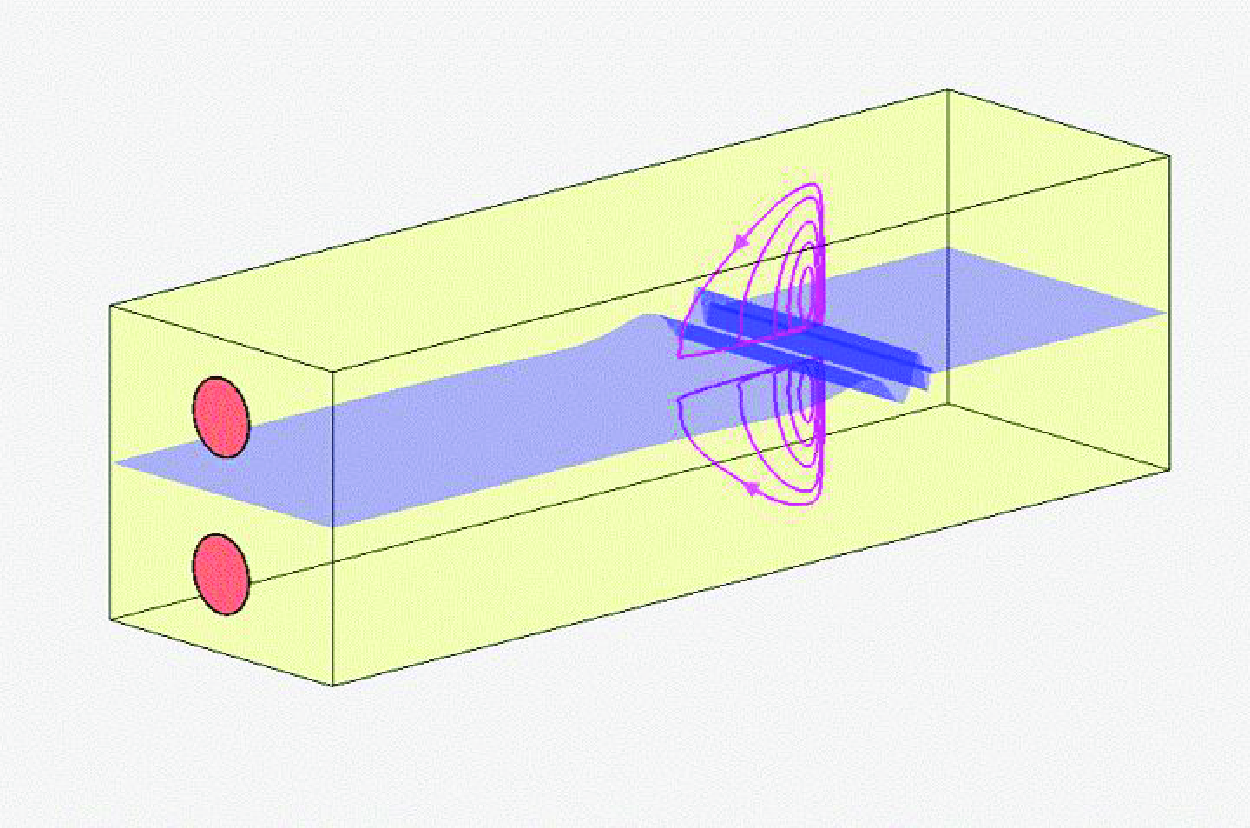
Sound entering the ear is known not only to transmit signals to the nerve system, but also to generate vortex-like steady streaming in the cochlea. This streaming has been suggested as the primary vehicle for drug delivery in the inner ear (Sumner, Mestel & Reichenbach, 2021, Sci. Rep., vol. 11, 57). An alternative vehicle by pure diffusion alone has also been suggested by Sadreev et al. (2019, Front. Cell. Neurosci., vol. 13, 161). This paper purports to examine both mechanisms analytically, and compare their relative importance, based on the two-dimensional model of Allen (1977, Acoust. Soc. Am., vol. 61, 110–119). First, we reconstruct the fluid mechanics of the Békséy vortices by an asymptotic theory of multiple scales as a complement to the two-dimensional numerical theory of Edom, Obrist & Kleiser (2014, J. Fluid Mech., vol. 753, 254–278). For discerning the difference between Sumner, Mestel & Reichenbach (2021) and Sadreev et al. (2019), we combine sound-induced streaming and molecular diffusion by modeling the drug as a solute of known diffusivity. It will be shown that due to the high frequency of sound, advection is augmented by the Lagrangian velocity, but molecular diffusion still dominates drug transport in the cochlear duct, unlike Taylor dispersion of pollutant by tides in a shallow river.
Information
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2025. Published by Cambridge University Press


