Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Tronko, N.
Nazarenko, S. V.
and
Galtier, S.
2013.
Weak turbulence in two-dimensional magnetohydrodynamics.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 87,
Issue. 3,
Tran, Chuong V.
Yu, Xinwei
and
Blackbourn, Luke A. K.
2013.
Two-dimensional magnetohydrodynamic turbulence in the limits of infinite and vanishing magnetic Prandtl number.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 725,
Issue. ,
p.
195.
Dritschel, David G.
2013.
Waves and Turbulence: Their Cooperative Role in Structure Formation.
Procedia IUTAM,
Vol. 8,
Issue. ,
p.
85.
Dritschel, David G.
Qi, Wanming
and
Marston, J. B.
2015.
On the late-time behaviour of a bounded, inviscid two-dimensional flow.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 783,
Issue. ,
p.
1.
Dritschel, David G.
and
McKiver, William J.
2015.
Effect of Prandtl’s ratio on balance in geophysical turbulence.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 777,
Issue. ,
p.
569.
Reinaud, Jean N.
Dritschel, David G.
and
Carton, Xavier
2016.
Interaction between a surface quasi-geostrophic buoyancy filament and an internal vortex.
Geophysical & Astrophysical Fluid Dynamics,
Vol. 110,
Issue. 6,
p.
461.
Gilbert, Andrew D.
Mason, Joanne
and
Tobias, Steven M.
2016.
Flux expulsion with dynamics.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 791,
Issue. ,
p.
568.
Jougla, Thibault
and
Dritschel, David G.
2017.
On the energetics of a two-layer baroclinic flow.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 816,
Issue. ,
p.
586.
Dritschel, David G.
Böing, Steven J.
Parker, Douglas J.
and
Blyth, Alan M.
2018.
The moist parcel‐in‐cell method for modelling moist convection.
Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society,
Vol. 144,
Issue. 715,
p.
1695.
Dritschel, D. G.
Diamond, P. H.
and
Tobias, S. M.
2018.
Circulation conservation and vortex breakup in magnetohydrodynamics at low magnetic Prandtl number.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 857,
Issue. ,
p.
38.
Dritschel, David G.
and
Jalali, Mohammad Reza
2019.
On the regularity of the Green–Naghdi equations for a rotating shallow fluid layer.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 865,
Issue. ,
p.
100.
Jalali, M. R.
and
Dritschel, D. G.
2021.
Balance in non-hydrostatic rotating shallow-water flows.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 8,
Frey, Matthias
Dritschel, David
and
Böing, Steven
2022.
EPIC: The Elliptical Parcel-In-Cell method.
Journal of Computational Physics: X,
Vol. 14,
Issue. ,
p.
100109.
Dritschel, Heidi J.
Dritschel, David G.
and
Carr, Magda
2023.
A conformal mapping approach to modelling two-dimensional stratified flow.
Journal of Computational Physics: X,
Vol. 17,
Issue. ,
p.
100129.
Padhan, Nadia Bihari
and
Pandit, Rahul
2025.
The Cahn–Hilliard–Navier–Stokes framework for multiphase fluid flows: laminar, turbulent and active.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 1010,
Issue. ,
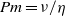 . When
. When  , the magnetic field dissipates at a scale much larger than the velocity field. The method we utilize is a novel hybrid contour–spectral method, the ‘combined Lagrangian advection method’, formally to integrate the equations with zero viscous dissipation. The method is compared with a standard pseudo-spectral method for decreasing
, the magnetic field dissipates at a scale much larger than the velocity field. The method we utilize is a novel hybrid contour–spectral method, the ‘combined Lagrangian advection method’, formally to integrate the equations with zero viscous dissipation. The method is compared with a standard pseudo-spectral method for decreasing 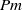 for the problem of decaying two-dimensional MHD turbulence. The method is shown to agree well for a wide range of imposed magnetic field strengths. Examples of problems for which such a method may prove invaluable are also given.
for the problem of decaying two-dimensional MHD turbulence. The method is shown to agree well for a wide range of imposed magnetic field strengths. Examples of problems for which such a method may prove invaluable are also given.