Article contents
Water entry of spheres with various contact angles
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 10 January 2019
Abstract
It is well known that the water entry of a sphere causes cavity formation above a critical impact velocity as a function of the solid–liquid contact angle; Duez et al. (Nat. Phys., vol. 3 (3), 2007, pp. 180–183). Using a rough sphere with a contact angle of 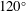 $120^{\circ }$, Aristoff & Bush (J. Fluid Mech., vol. 619, 2009, pp. 45–78) showed that there are four different cavity shapes dependent on the Bond and Weber numbers (i.e., quasistatic, shallow, deep and surface). We experimentally alter the Bond number, Weber number and contact angle of smooth spheres and find two key additions to the literature: (1) cavity shape also depends on the contact angle; (2) the absence of a splash crown at low Weber number results in cavity formation below the predicted critical velocity. In addition, we use alternate scales in defining the Bond, Weber and Froude numbers to predict the cavity shapes and scale pinch-off times for various impacting bodies (e.g., spheres, multidroplet streams and jets) on the same plots, merging the often separated studies of solid–liquid and liquid–liquid impact in the literature.
$120^{\circ }$, Aristoff & Bush (J. Fluid Mech., vol. 619, 2009, pp. 45–78) showed that there are four different cavity shapes dependent on the Bond and Weber numbers (i.e., quasistatic, shallow, deep and surface). We experimentally alter the Bond number, Weber number and contact angle of smooth spheres and find two key additions to the literature: (1) cavity shape also depends on the contact angle; (2) the absence of a splash crown at low Weber number results in cavity formation below the predicted critical velocity. In addition, we use alternate scales in defining the Bond, Weber and Froude numbers to predict the cavity shapes and scale pinch-off times for various impacting bodies (e.g., spheres, multidroplet streams and jets) on the same plots, merging the often separated studies of solid–liquid and liquid–liquid impact in the literature.
JFM classification
- Type
- JFM Rapids
- Information
- Copyright
- © 2019 Cambridge University Press
References
Speirs et al. supplementary movie 1
A 3 mm diameter sphere impacts a quiescent pool surface with velocity Uo=4.43 m/s and static contact angle θ=101.0˚ without forming a cavity. The movie is played back at 0.6% of real speed.
Speirs et al. supplementary movie 2
A 3 mm diameter sphere impacts a quiescent pool surface with velocity Uo=0.24 m/s and static contact angle θ=141.1˚ forming a quasi-static seal cavity. The movie is played back at 0.6% of real speed.
Speirs et al. supplementary movie 3
A 3 mm diameter sphere impacts a quiescent pool surface with velocity Uo=1.40 m/s and static contact angle θ=141.1˚ forming a shallow seal cavity. Deep seal quickly follows shallow seal in this case. The movie is played back at 0.6% of real speed.
Speirs et al. supplementary movie 4
A 3 mm diameter sphere impacts a quiescent pool surface with velocity Uo=2.80 m/s and static contact angle θ=141.1˚ forming a deep seal cavity. The movie is played back at 0.6% of real speed.
- 62
- Cited by


