Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Rodenborn, Bruce
Chen, Chih-Hung
Swinney, Harry L.
Liu, Bin
and
Zhang, H. P.
2013.
Propulsion of microorganisms by a helical flagellum.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,
Vol. 110,
Issue. 5,
Tabak, A.F.
and
Yesilyurt, S.
2014.
Computationally-validated surrogate models for optimal geometric design of bio-inspired swimming robots: Helical swimmers.
Computers & Fluids,
Vol. 99,
Issue. ,
p.
190.
Cheang, U Kei
Meshkati, Farshad
Kim, Dalhyung
Kim, Min Jun
and
Fu, Henry Chien
2014.
Minimal geometric requirements for micropropulsion via magnetic rotation.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 90,
Issue. 3,
Meshkati, Farshad
and
Fu, Henry Chien
2014.
Modeling rigid magnetically rotated microswimmers: Rotation axes, bistability, and controllability.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 90,
Issue. 6,
Kanehl, Philipp
and
Ishikawa, Takuji
2014.
Fluid mechanics of swimming bacteria with multiple flagella.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 89,
Issue. 4,
Tabak, Ahmet Fatih
and
Yesilyurt, Serhat
2014.
Improved Kinematic Models for Two-Link Helical Micro/Nanoswimmers.
IEEE Transactions on Robotics,
Vol. 30,
Issue. 1,
p.
14.
Gao, Zhiyong
Li, He
Chen, Xiao
and
Zhang, H. P.
2015.
Using confined bacteria as building blocks to generate fluid flow.
Lab on a Chip,
Vol. 15,
Issue. 24,
p.
4555.
Elgeti, J
Winkler, R G
and
Gompper, G
2015.
Physics of microswimmers—single particle motion and collective behavior: a review.
Reports on Progress in Physics,
Vol. 78,
Issue. 5,
p.
056601.
Barry, Michael T.
Rusconi, Roberto
Guasto, Jeffrey S.
and
Stocker, Roman
2015.
Shear-induced orientational dynamics and spatial heterogeneity in suspensions of motile phytoplankton.
Journal of The Royal Society Interface,
Vol. 12,
Issue. 112,
p.
20150791.
Patteson, A. E.
Gopinath, A.
Goulian, M.
and
Arratia, P. E.
2015.
Running and tumbling with E. coli in polymeric solutions.
Scientific Reports,
Vol. 5,
Issue. 1,
Deepika, Deepti
Karmakar, Richa
Tirumkudulu, Mahesh S.
and
Venkatesh, K. V.
2015.
Variation in swimming speed of Escherichia coli in response to attractant.
Archives of Microbiology,
Vol. 197,
Issue. 2,
p.
211.
Yang, Chengpeng
Hu, Dinglong
Sun, Baoce
Cui, Xin
Zhu, Qian
and
Lam, Raymond H. W.
2015.
Mixing in an enclosed microfluidic chamber through moving boundary motions.
Microfluidics and Nanofluidics,
Vol. 19,
Issue. 3,
p.
711.
Gonzalez, O.
2015.
A Theorem on the Surface Traction Field in Potential Representations of Stokes Flow.
SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics,
Vol. 75,
Issue. 4,
p.
1578.
Fu, Henry C.
Jabbarzadeh, Mehdi
and
Meshkati, Farshad
2015.
Magnetization directions and geometries of helical microswimmers for linear velocity-frequency response.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 91,
Issue. 4,
Espeso, David R.
Martínez-García, Esteban
de Lorenzo, Víctor
and
Goñi-Moreno, Ángel
2016.
Physical Forces Shape Group Identity of Swimming Pseudomonas putida Cells.
Frontiers in Microbiology,
Vol. 7,
Issue. ,
Karmakar, Richa
Uday Bhaskar, R. V. S.
Jesudasan, Rajesh E.
Tirumkudulu, Mahesh S.
Venkatesh, K. V.
and
Kivisaar, M.
2016.
Enhancement of Swimming Speed Leads to a More-Efficient Chemotactic Response to Repellent.
Applied and Environmental Microbiology,
Vol. 82,
Issue. 4,
p.
1205.
Constantino, Maira A.
Jabbarzadeh, Mehdi
Fu, Henry C.
and
Bansil, Rama
2016.
Helical and rod-shaped bacteria swim in helical trajectories with little additional propulsion from helical shape.
Science Advances,
Vol. 2,
Issue. 11,
Martindale, J. D.
Jabbarzadeh, M.
and
Fu, H. C.
2016.
Choice of computational method for swimming and pumping with nonslender helical filaments at low Reynolds number.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 28,
Issue. 2,
Lauga, Eric
2016.
Bacterial Hydrodynamics.
Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 48,
Issue. 1,
p.
105.
Martínez, Laura E.
Hardcastle, Joseph M.
Wang, Jeffrey
Pincus, Zachary
Tsang, Jennifer
Hoover, Timothy R.
Bansil, Rama
and
Salama, Nina R.
2016.
Helicobacter pylori strains vary cell shape and flagellum number to maintain robust motility in viscous environments.
Molecular Microbiology,
Vol. 99,
Issue. 1,
p.
88.
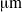 . For this bacterium, we show that flagellar bundles with fixed orientation relative to the cell body are unlikely to produce wiggling trajectories with pitch larger than 4
. For this bacterium, we show that flagellar bundles with fixed orientation relative to the cell body are unlikely to produce wiggling trajectories with pitch larger than 4 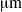 . An estimate based on torque balance shows that this constraint on pitch is a result of the large torque exerted by the flagellar bundle. On the other hand, multiple rigid bundles with fixed orientation, similar to those recently observed experimentally, are able to produce wiggling trajectories with large pitches.
. An estimate based on torque balance shows that this constraint on pitch is a result of the large torque exerted by the flagellar bundle. On the other hand, multiple rigid bundles with fixed orientation, similar to those recently observed experimentally, are able to produce wiggling trajectories with large pitches.