Published online by Cambridge University Press: 07 November 2019
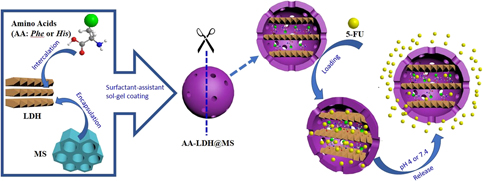
A nanoparticle-based drug delivery system is first established by mesoporous silica encapsulating amino acid–intercalated layered double hydroxide (LDH) to construct nanocomposites AA-LDH@MS. The amino acids including phenylalanine (Phe) and histidine (His) with aromatic groups are intercalated into LDH as the cores Phe-LDH and His-LDH. These nanocomposites AA-LDH@MS display multispaces of the interlayer spaces of LDH and porous channels of mesoporous silica to load drugs. Moreover, amino acid molecules provide the interaction sites to improve effectively loading amounts of drugs. 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) is used as the cargo molecules to observe the delivery in vitro. The results indicate that the maximum loading amounts of drugs are up to 392 mg/g at 60 °C for 12 h in the nanocomposite Phe-LDH@MS. All the nanocomposites exhibit the sustained release of 5-FU at pH 4 and pH 7.4. The Korsmeyer–Peppas model is used to fit the kinetic plot of the drug release in vitro, which concludes that 5-FU release from AA-LDH@MS belongs to Fickian diffusion.