Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Lee, Doh-Kwon
and
Yoo, Han-Ill
2006.
Electron-Ion Interference and Onsager Reciprocity in Mixed Ionic-Electronic Transport inTiO2.
Physical Review Letters,
Vol. 97,
Issue. 25,
Hong, Jeong Oh
and
Yoo, H.I.
2006.
Electric Field-Induced Unmixing in Mixed Ferrite Spinel (Co,Fe)<sub>3</sub>O<sub>4</sub>.
Vol. 46,
Issue. ,
p.
11.
Weiss, B.
Sturn, J.
Winter, F.
and
Schenk, J. L.
2009.
Empirical reduction diagrams for reduction of iron ores with H2and CO gas mixtures considering non-stoichiometries of oxide phases.
Ironmaking & Steelmaking,
Vol. 36,
Issue. 3,
p.
212.
Chatzichristodoulou, Christodoulos
Park, Woo-Seok
Kim, Hong-Seok
Hendriksen, Peter Vang
and
Yoo, Han-Ill
2010.
Experimental determination of the Onsager coefficients of transport for Ce0.8Pr0.2O2−δ.
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics,
Vol. 12,
Issue. 33,
p.
9637.
Kim, Hong-Seok
and
Yoo, Han-Ill
2010.
Complete representation of isothermal mass and charge transport properties of mixed ionic–electronic conductor La2NiO4+δ.
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics,
Vol. 12,
Issue. 40,
p.
12951.
Yoo, H.-I.
and
Kim, H.-S.
2012.
Complete representation of isothermal mass and charge transport properties of mixed ionic electronic conductors.
Solid State Ionics,
Vol. 225,
Issue. ,
p.
166.
Sun, Jia-Lin
Zhang, Wei
Wei, Jinquan
and
Gu, Bingfu
2014.
Ion-modulated nonlinear electronic transport in carbon nanotube bundle/RbAg4I5 thin film composite nanostructures.
Journal of Applied Physics,
Vol. 115,
Issue. 4,
Riess, I.
2015.
Reply to the ‘Comment on “How to interpret Onsager cross terms in mixed ionic electronic conductors”’ by H.-I. Yoo, M. Martin, and J. Janek, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,7, DOI: 10.1039/C4CP05737F.
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics,
Vol. 17,
Issue. 16,
p.
11107.
Yoo, Han-Ill
Martin, Manfred
and
Janek, Juergen
2015.
Comment on “How to interpret Onsager cross terms in mixed ionic electronic conductors” by I. Riess, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014,16, 22513.
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics,
Vol. 17,
Issue. 16,
p.
11103.
Liu, Yu
Yin, Jun
Wang, Pengfei
Zhu, Jin-Lin
Ma, Wanyun
Dong, Zhanmin
and
Sun, Jia-Lin
2018.
Broadband photoresponse based on a synergistic effect of surface ions and plasmon polaritons.
Journal of Materials Chemistry C,
Vol. 6,
Issue. 5,
p.
1199.
Ju, Misong
Cho, Ouk Hyun
Lee, Jaehun
Namgung, Seok Daniel
Song, Min-Kyu
Balamurugan, Mani
Kwon, Jang-Yeon
and
Nam, Ki Tae
2020.
Quantitative analysis of the coupling between proton and electron transport in peptide/manganese oxide hybrid films.
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics,
Vol. 22,
Issue. 14,
p.
7537.
Yoo, Han-Ill
2025.
Transient-state methods to determine all the mass/charge transport properties of a material.
Solid State Ionics,
Vol. 430,
Issue. ,
p.
116998.
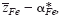 of mobile cations (Fe2+, Fe3+) in semiconducting Fe3O4 was determined at elevated temperatures via Tubandt-type electrotransport experiments in association with the literature data on the cation diffusivity and total electrical conductivity. It has been found that the value for
of mobile cations (Fe2+, Fe3+) in semiconducting Fe3O4 was determined at elevated temperatures via Tubandt-type electrotransport experiments in association with the literature data on the cation diffusivity and total electrical conductivity. It has been found that the value for 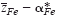 varies systematically from below 2 up to 3 with oxygen partial pressure at a fixed temperature. The effective valence is determined not only by the mobility difference of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions
varies systematically from below 2 up to 3 with oxygen partial pressure at a fixed temperature. The effective valence is determined not only by the mobility difference of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions 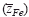 but also by the cross effect between the cations and electrons upon their transfer
but also by the cross effect between the cations and electrons upon their transfer 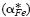 . A value of
. A value of 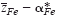 between 2 and 3 may be attributed to the mobility difference between Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions even in the absence of the cross effect, but the values of
between 2 and 3 may be attributed to the mobility difference between Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions even in the absence of the cross effect, but the values of 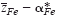 < 2 clearly indicate that the cross effect is in play in Fe3O4.
< 2 clearly indicate that the cross effect is in play in Fe3O4.
