Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 June 2012
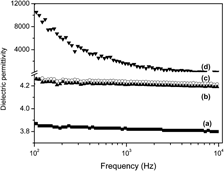
High permittivity antimony-doped tin oxide (ATO)/polyimide (PI) composite films consisting of narrow size distribution ATO fillers prepared by inverse microemulsion method and PI host are synthesized by in situ polymerization. The microstructure and thermal stability of composite films are characterized by scanning electron microscopy and thermal gravimetric analyses, respectively. Dielectric properties of composite films with different concentrations of ATO particles of variable size are investigated in the frequency range of 102 to 2.5 × 106 Hz. The hydrophilic surface of ATO is not helpful of tight connection between the filler and host. The addition of ATO contributes slight increase of the thermal stability. However, the permittivity of composite films can be remarkably increased due to Maxwell–Wagner–Sillars polarization as well as a large number of tiny capacitors formed by ATO particles with narrow distribution and small size. The dielectric constant behavior of composite films fits well to the usual percolation theory.