No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 October 2016
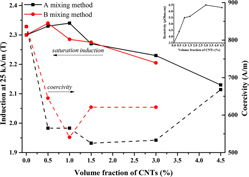
Different volume fractions (0.5–4.5 vol%) of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) were used to reinforce a binary Fe50Co soft magnetic alloy. The first method for dispersion involved dry mixing and ball milling of the powder, while the second included wet mixing in dimethylformamide under ultrasonic agitation, drying and then dry ball milling. The powders were consolidated using spark plasma sintering. Tensile test and SEM analyses were performed to characterize the mechanical properties and the fracture surface of the sintered materials. The best magnetic and mechanical properties were achieved using the first method. A maximum enhancement in tensile strength of around 20% was observed in the 0.5 vol% CNT composite with improved elongation compared to the monolithic Fe50Co alloy. In addition, the magnetic properties were enhanced by adding CNTs up to 1 vol%, and an improvement in densification was observed in composites up to 1.5 vol% CNT with respect to monolithic Fe50Co alloy.
Contributing Editor: Jürgen Eckert