Article contents
Preparation and microwave absorption properties of Ni/rGO/EP composite foam
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 11 June 2020
Abstract
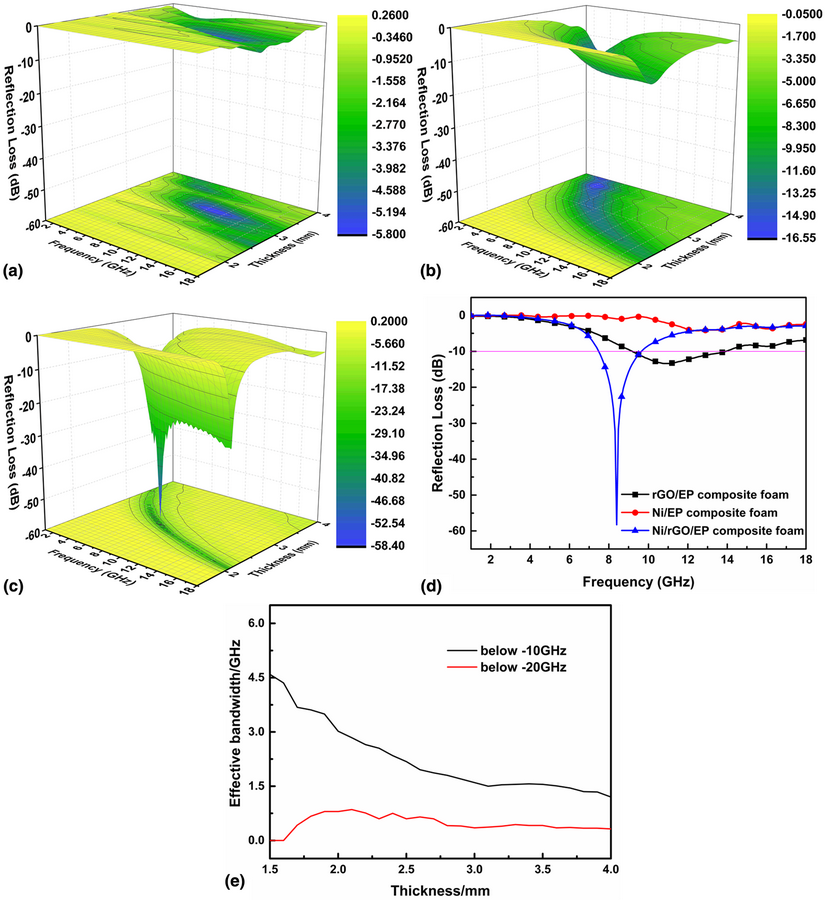
In this study, the Ni/rGO hollow microspheres were synthesized and combined with epoxy foam to prepare structural absorbing materials. The diameter of obtained rGO hollow microspheres loaded with Ni nanoparticles was around 10 μm and the thickness of the spherical wall was about 70 nm. The Ni/rGO/EP composite foam exhibited better microwave absorption properties than that of rGO/EP and Ni/EP composite foam. The minimum reflection loss value (RLmin) could reach −58.23 dB at 8.4 GHz with a thickness of 2.5 mm, and the effective bandwidth with RLmin lower than −10 dB is 2.21 GHz ranging from 7.46 to 9.67 GHz. The porous structure of Ni/rGO hollow microspheres and their filled epoxy foam can refract and absorb the electromagnetic waves repeatedly, which equals to extend the propagation path of microwave, thus, electromagnetic loss capacity was improved obviously.
Information
- Type
- Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2020
References
- 7
- Cited by


