No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 April 2016
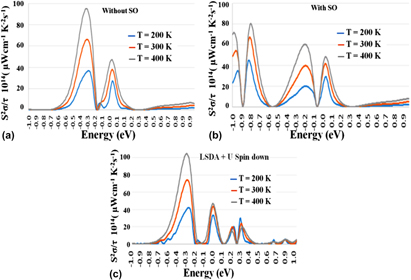
The discovery of Heusler alloys has revolutionized the research field of intermetallics due to the ease with which one can derive potential candidates for multifunctional applications. During recent years, many half Heusler alloys have been investigated for their thermoelectric properties. The f-electron-based rare-earth ternary half Heusler compound DyPdBi has its f energy levels located close to the Fermi energy level. Other research efforts have emphasized that such materials have good thermoelectric capabilities. We have explored using first principles the electronic band structure of DyPdBi by use of different exchange correlation potentials in the density functional theoretical framework. Transport coefficients that arise in the study of thermoelectric properties of DyPdBi have been calculated and have illustrated its potential as an efficient thermoelectric material. Both the theoretically estimated Seebeck coefficient and the power factor agree well with the available experimental results. Our calculations illustrate that it is essential to include spin–orbit coupling in these models of f-electron half Heusler materials.