Published online by Cambridge University Press: 03 November 2016
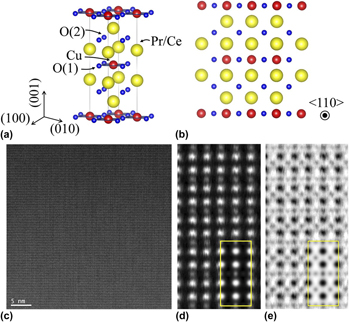
Pr2−x Cex CuO4+δ thin films were grown hetero-epitaxially on (001) SrTiO3 substrates using ozone-assisted molecular beam epitaxy. High-quality epilayers with a cerium concentrations of x = 0.15 were grown and characterized electrically, structurally, and by magnetization measurements. The Pr2−x Cex CuO4+δ films were found to maintain the tetragonal Nd2CuO4 (T′) crystal structure with a linear dependence of lattice constant on the Ce concentration. The superconductivity of the Pr2−x Cex CuO4+δ films was maintained up to x ≈ 0.23 with a T c up to 12.6 K. For x < 0.15, control of the oxygen concentration δ by annealing is crucial for the induction of superconductivity in Pr2−x Cex CuO4+δ and this still holds for x > 0.20. We show that the electron mean free path length  $\ell$ may be significantly enhanced by optimizing those annealing conditions. Moreover, the enhancement of
$\ell$ may be significantly enhanced by optimizing those annealing conditions. Moreover, the enhancement of  $\ell$ leads to a reduction of the upper critical field, suggesting that superconductivity of Pr2−x Cex CuO4+δ is to be considered in the clean limit.
$\ell$ leads to a reduction of the upper critical field, suggesting that superconductivity of Pr2−x Cex CuO4+δ is to be considered in the clean limit.