Article contents
Detailed investigation of contact deformation in ZrN/Zr multiplayer—understanding the role of volume fraction, bilayer spacing, and morphology of interfaces
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 19 November 2013
Abstract
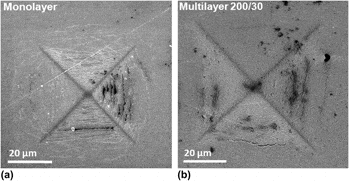
A systematic study was done to understand the influence of volume fractions and bilayer spacings for metal/nitride multilayer coating using finite element method (FEM). An axisymmetric model was chosen to model the real situation by incorporating metal and substrate plasticity. Combinations of volume fractions and bilayer spacings were chosen for FEM analysis consistent with experimental results. The model was able to predict trends in cracking with respect to layer spacing and volume fraction. Metal layer plasticity is seen to greatly influence the stress field inside nitride. It is seen that the thicker metal induces higher tensile stresses inside nitride and hence leads to lower cracking loads. Thin metal layers <10 nm were seen to have curved interfaces, and hence, the deformation mode was interfacial delamination in combination with edge cracking. There is an optimum seen with respect to volume fraction ∼13% and metal layer thickness ∼30 nm, which give maximum crack resistance.
Information
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2013
References
REFERENCES
- 8
- Cited by

