Article contents
Development of tensile-compressive asymmetry free magnesium based composite using TiO2 nanoparticles dispersion
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 November 2017
Abstract
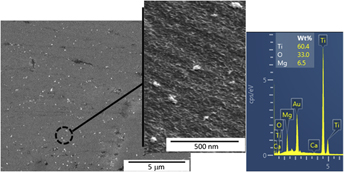
In this present study, different volume percentages of titanium dioxide nanoparticles were added as dispersions in commercially pure magnesium using the blend-press-sinter powder metallurgy process followed by hot extrusion. The physically blended titanium dioxide nanoparticles dispersoid induced a significant grain refinement in the extruded magnesium matrix. Characterization of the mechanical properties revealed that the increasing volume percentage of titanium oxide nanoparticles dispersion was effective in enhancing the ductility of magnesium without disturbing the strength under tensile loading and enhancing the strength of magnesium without disturbing the ductility under compressive loading. The dominating deformation mechanism in pure magnesium was the dislocation slip, which was subdued by the tensile twinning deformation mechanism due to the increasing presence of titanium dioxide dispersion. The effect of shift in the dominating deformation mechanism was displayed by the elimination of tensile-compressive asymmetry in magnesium when dispersed with 1 vol% of titanium dioxide nanoparticles.
Information
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2017
Footnotes
Contributing Editor: Yang-T. Cheng
References
REFERENCES
- 10
- Cited by


