Published online by Cambridge University Press: 02 December 2011
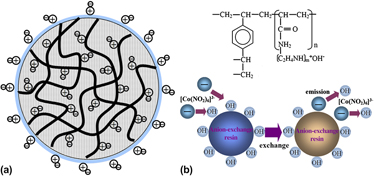
Graphitic carbon (GC) is prepared using an ion-exchange resin as carbon source at 600 °C. A Co salt is selected as the graphitization catalyst and is pre-exchanged onto the resin during the ion-exchange process. The GC is characterized by transmission electron microscopy, x-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, and thermogravimetry. Analysis of the crystallization shows that graphitization can occur at a temperature of as low as 600 °C, compared to the usual temperature of above 2000 °C in industry and above 1000 °C in literature. Different carbon structures have been found for different pretreatments of the resin and different heat treatment temperatures. This energy-saving method is an important breakthrough for the economic mass production of GC.