No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 23 November 2011
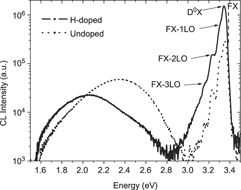
ZnO crystals have been investigated by scanning cathodoluminescence microscopy and spectroscopy at 80 K following hydrogen incorporation by plasma exposure. The intensity of the ZnO near-band-edge (NBE) emission is greatly enhanced while the defect-related green emission is quenched following plasma treatment. These effects are attributed to the passivation of zinc vacancies by hydrogen. The green and yellow intensities and their intensity ratios to the NBE vary with excitation depth for both undoped and H-doped ZnO crystals. The intensities of the green and yellow emissions exhibit sublinear dependencies on electron beam excitation density while the NBE intensity increases linearly with the excitation density. These saturation effects with increasing excitation density must be taken into account when assessing defects in ZnO by luminescence characterization.