Published online by Cambridge University Press: 07 May 2015
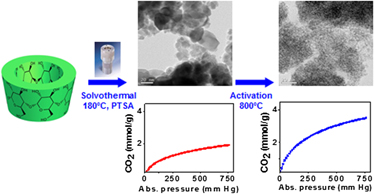
Microporous carbon nanospheres were prepared from β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) by solvothermal carbonization in o-dichlorobenzene in the presence of various concentrations of p-toluene sulfonic acid (PTSA). The contribution of PTSA toward solvothermal char (STC) was established. The STC showed the highest surface area, porosity, and CO2 sorption capacity at a PTSA to β-CD weight ratio of 2.5. The surface area, pore volume, and CO2 sorption capacity were further increased by an in situ high-temperature activation due to the oxidation of carbon at high temperature by oxygen present in the STC. The high-temperature activation reduces the significance of PTSA concentration, as the activated STC showed surface area, micropore volume, and CO2 adsorption capacity in a close range at the PTSA to β-CD weight ratio in the range of 0.04–2.50. The highest CO2 adsorption capacity of the STC increased from 2.4 to 3.5 mmol/g upon the high-temperature activation. The activated STC adsorbs significant amount (0.35 mmol/g) of CO2 from dry air containing 400 ppm CO2. The activated STC showed excellent regeneration stability and selectivity over nitrogen.
Contributing Editor: Paolo Colombo