Article contents
Effects of Zn content on microstructures and mechanical properties of as-cast Mg–4Y–xZn alloys
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 07 August 2017
Abstract
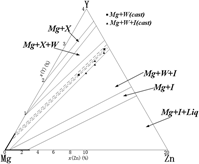
Effects of Zn content on microstructures and mechanical properties of as-cast Mg–4Y–xZn alloys (x = 1, 2, 3, 4) have been studied in the article. The results indicate that the X phase is formed firstly, and the X phase, X + W phases, and W phase precipitated in order when the Zn contents increased from 1 to 4 wt%. The secondary dendritic arm spacing of the tested alloys first decrease as the Zn content increases within the range of 1–2% and then it increases. The ultimate tensile strength (UTS) and elongation of the four experimental alloys increase until the addition of Zn reaches to 3%, with the maximum values of 213.6 MPa and 11.82%, respectively. Besides, the fracture behaviors of Mg–4Y–1Zn, Mg–4Y–2Zn, and Mg–4Y–3Zn were a quasi-cleavage fracture, while Mg–4Y–4Zn belonged to cleavage.
Information
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2017
Footnotes
Contributing Editor: Jürgen Eckert
References
REFERENCES
- 4
- Cited by


