Published online by Cambridge University Press: 10 May 2013
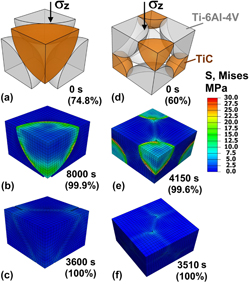
Ti-6Al-4V alloy with attractive properties such as corrosion resistance and high specific strength has a broad impact on daily life in the field of aerospace and medicine. The addition of TiC to Ti-6Al-4V is to further improve abrasion resistance and hardness. To have a low processing cost and precise control of the TiC volume fraction and distribution, the composite is densified with a blend of Ti-6Al-4V and TiC powders through a powder metallurgy route. The densification kinetics of the blend is studied for uniaxial die pressing (i) under isothermal conditions at 1020 °C, where β-Ti-6Al-4V deforms by creep and (ii) upon thermal cycling from 860 to 1020 °C, where the α-β transformation leads to transformation superplasticity. Densification curves for both isothermal and thermal cycling for various applied stresses and TiC fractions are in general agreement with predictions from continuum models and finite element simulation models performed at the powder level.