Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 October 2020
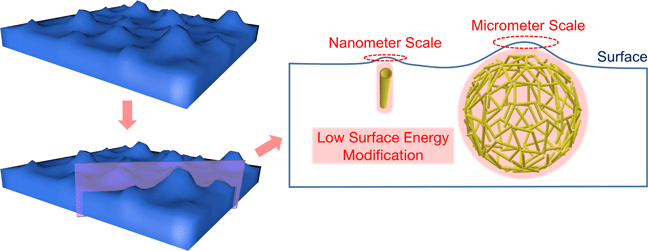
The construction of halloysite spherical capsules (halloysite aerogels) was reported for the first time in our previous work. The excellent performance of the microcapsule in functional carrying was also found in our further research. In this work, the anti-icing surface was fabricated by using halloysite nanotubes and halloysite spherical microcapsules. The fabrication of the anti-icing coating was investigated, and the ice nucleation behavior of droplet on the coating surface was studied. The modified halloysite nanotubes (F-HNTs) and the modified halloysite microcapsules (F-HAs) were characterized by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, thermal gravimetric, and pore size distribution. The results show that the introduction of F-HNTs and F-HAs have successfully formed a micro-nano structure on the coating surface with superhydrophobicity performance. The icing temperature of the coating has decreased 2.3 °C compared with bare glass, and the ice adhesion strength has decreased 82%. According to the ice dynamic mechanics, the ice nucleation rate on the coating is significantly reduced, thus the halloysite microcapsule coating has good icephobic performance.