No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 25 July 2014
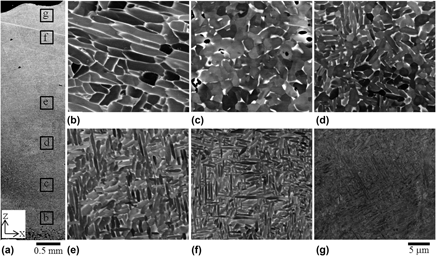
Ti–6Al–4V parts made by the additive manufacturing (AM) technique selective laser melting (SLM) generally show poor ductility due to their fine martensitic microstructure. This study was designed to assess whether a more suitable microstructure can be obtained when long laser/material interaction times are used. As-fabricated components with an α + β microstructure were produced and characterized with various microscopy techniques. The microstructural evolution was discussed in relation to the build platform temperature, the cyclic reheating, and the thermal stresses that developed during the process. The hardness of the samples was also evaluated and discussed. The hardness varied in relation to the different microstructure morphologies observed in the samples and different partitioning of the alloying elements. This study indicates a methodology through SLM to obtain Ti–6Al–4V with an as-deposited α + β microstructure which is more desirable than that the typical fully martensitic microstructure typically obtained after SLM.