No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 11 June 2020
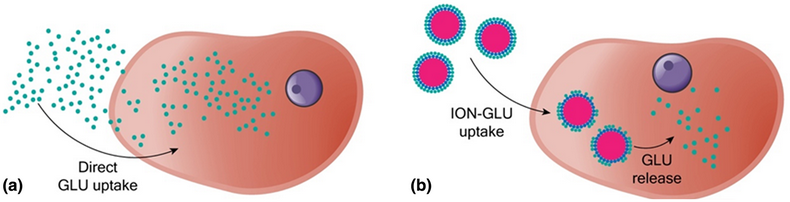
Herein, we report a synthetic route capable of producing superparamagnetic, stable and biocompatible glucosamine (GLU) nanocarriers, composed by colloidal iron oxide nanoparticles (ION, ~6 nm) surface-functionalized with GLU dispersed in physiological media (pH 7.2). The route consists first of the preparation of ION by aqueous alkaline co-precipitation of 1:2 Fe(II)/Fe(III) followed by surface treatment with citric acid, activation of acidic groups via carbodiimide intermediary and further amidation using GLU as the amine reactant. Results from cell viability tests performed with human dental pulp tissue cells suggest that ION–GLU nanocolloids are biocompatible and non-toxic for two different concentrations and several hours of incubation. Moreover, optical microscopy shows that ION–GLU adsorbs at the cells walls and also transposes them, reaching cytoplasm and nucleus as well. All findings point out the promising use of ION–GLU as biocompatible nanocarriers for GLU delivery such as in articulation diseases.