Published online by Cambridge University Press: 24 July 2017
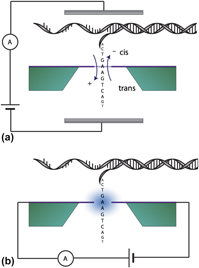
Nanoscale biosensor technology has attracted considerable attention with its promise of revolutionizing techniques ranging from biological interfaces to rapid pathogen detection to enabling DNA data storage. Many approaches, such as nanopore sequencing, have been explored and are already achieving tremendous success; however, new sensing modalities and architectures are emerging that are envisioned for the next generation of ever more capable biosensors. These novel devices, combined with advances in machine learning, are moving concepts from simulation to experimentation and demonstration. In recent years, rapid advances have been made and many architectures have been put forward for novel approaches to biomolecular sensing using nanoelectronics, including the advent of tunnel junctions as a sensing platform. With high accuracy, sensitivity, and affordability, these sensors are predicted to drive a shift to personalized medicine and rapid diagnostics in real-time anywhere in the world. Here we give an overview of tunneling sequencing and its application in biomolecular sensing and provide a perspective on the use of scalable tunneling sequencing methods utilizing graphene as the active component.
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Contributing Editor: Venkatesan Renugopalakrishnan