Published online by Cambridge University Press: 07 April 2020
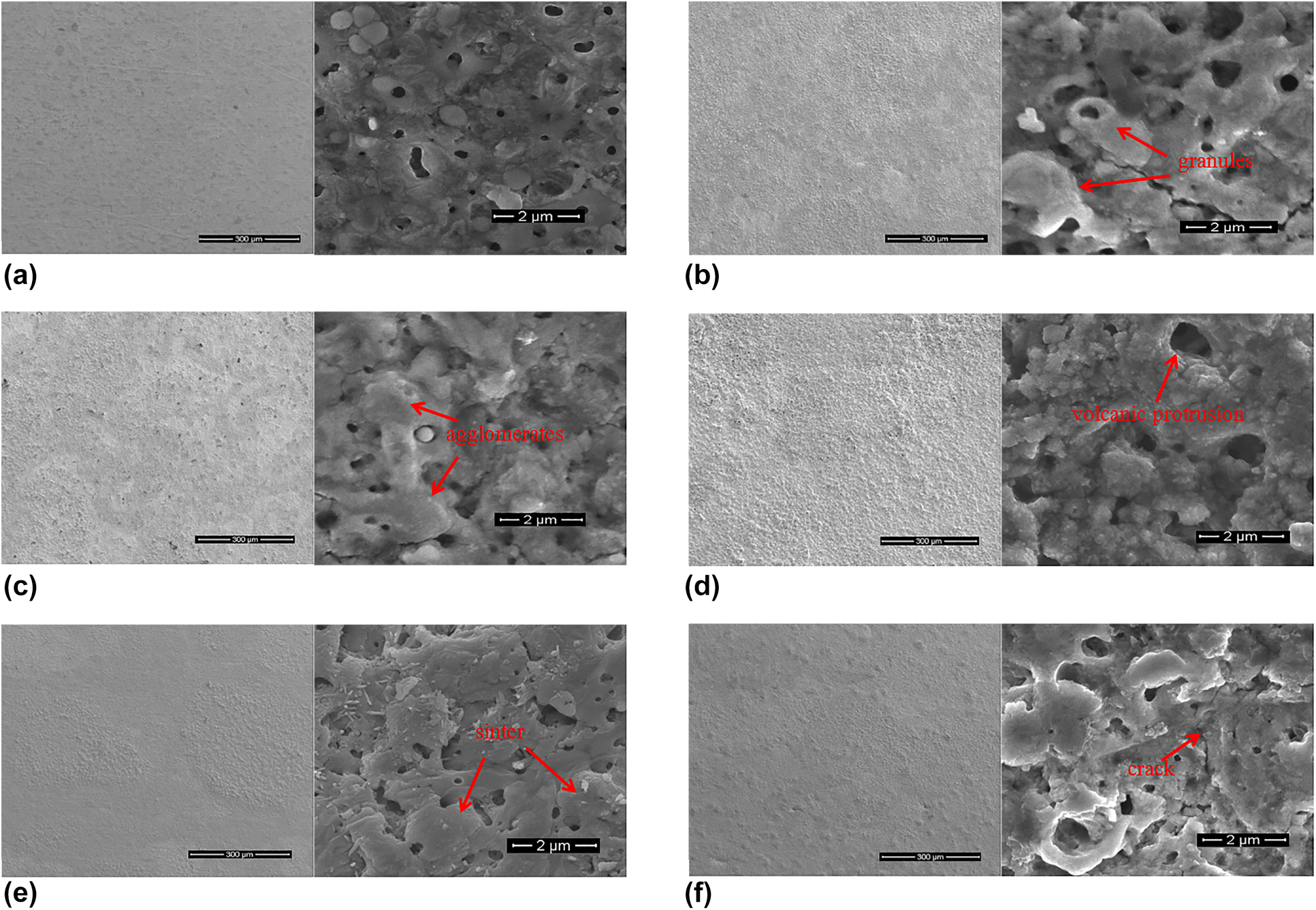
BaxSr(1−x)TiO3 (BST) thin films were fabricated on a Ti substrate using micro-arc oxidation (MAO) in an aqueous solution with the addition of 0.6 M Ba(OH)2, 0.4 M Sr(OH)2, and 0.05 M EDTA. The morphology, composition, and electrical properties of BST films prepared under different processing times were characterized, and MAO growth characteristics of BST films were discussed. Results indicate that dielectric and ferroelectric properties of BST films are positively correlated with surface morphology dependent on MAO spark patterns. To obtain a smooth and compact film, the large spark stage should be avoided. During MAO processes, elements from the substrate and electrolyte solution migrate in opposite directions under an electric field, resulting in Ba, Sr, Ti, and O elements exhibiting a gradient distribution between the BST film and the Ti substrate. BST film prepared using MAO is composed of two layers: an outer loose layer and an inner dense layer. In addition, because of the position of discharge breakdown continually changing, the interface between the film and the substrate is uneven. As MAO processing time increases, BST film thickness increases and ferroelectric property improves. When processing time is 15 min, the residual polarization intensity (2Pr) of the BST film is about 4.9 μC/cm2.