No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 10 January 2019
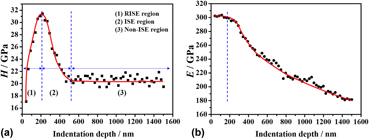
Highly dense zirconia dental ceramic coatings were fabricated by aqueous electrophoretic deposition (EPD) and subsequently sintered between 1250 and 1450 °C. Microstructural examination revealed that aqueous EPDZrO2 coatings possessed a tetragonal phase structure and the grain size increased with increasing sintering temperature. Nanoindentation study proved that the aqueous EPDZrO2 coating also had excellent mechanical properties. The effect of different applied loads on hardness and elastic modulus of the 1350 °C-sintered sample at room temperature was investigated by the method of progressive multicycle measurement nanoindentation. The simulative experiment proved that hardness of aqueous EPDZrO2 exhibited reverse indentation size effect (ISE) behavior and then displayed the normal ISE response. The analysis indicates that the reverse ISE is attributed to the relaxation of surface stresses resulting from indentation cracks at small loads and normal ISE is caused by geometrically necessary dislocations. The tetragonal–monoclinic stress-induced phase transformation during nanoindentation is the primary cause of dental zirconia failures.