Article contents
Investigation of local brittle zone in multipass welded joint of NiCrMoV steel with heavy section
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 26 February 2018
Abstract
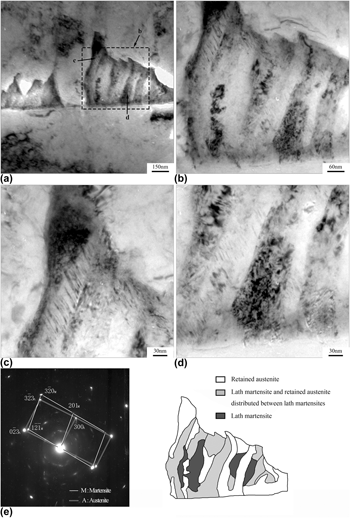
Welding was successfully used in the fabrication of low pressure steam turbine rotors for nuclear power plants. In this paper, the local brittle zone of the welded joint in NiCrMoV steel with heavy section was investigated by cross-zone fracture toughness test and the effect of martensite–austenite constituent in the simulated reheated zone of welds with different second peak temperature on toughness was analyzed. The results showed that the crack propagated in unstable manner in the reheated zone of welds where the martensite–austenite constituent promoted the initiation and propagation of the crack. The fine structure of martensite–austenite constituent contained retained austenite, martensite, and martensite–austenite mixture microstructure. The impact toughness deteriorated drastically in the incomplete phase transition zone for the simulated reheated zone of welds related to the formation of mixture microstructure in which large blocky martensite–austenite constituent at prior austenite grain boundaries and inside the grains were distributed in the shape of network.
- Type
- Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2018
Footnotes
Contributing Editor: Jürgen Eckert
References
REFERENCES
- 6
- Cited by


