Published online by Cambridge University Press: 07 February 2012
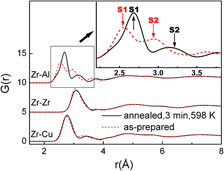
Atomic structures of the Zr48Cu45Al7 as-prepared and annealed metallic glasses (MGs) were investigated by performing the reverse Monte Carlo simulation on the synchrotron radiation-based experiments. It was found that although the annealed sample remains completely amorphous, the volumes of the Al-centered clusters evidently expand, which is attributed to the relatively longer Al–Zr bonds. As a result, the role of Al atoms as the glue atoms to connect and fix the Zr- and Cu-centered large clusters is accordingly weakened, which leads to the ease of the rearrangement of atoms and clusters in the glass state. This study provides an insight into the microstructures of MGs, which extends understanding of the structural evolution in the glass alloys during annealing prior to the precipitation of nanocrystals.