Published online by Cambridge University Press: 18 May 2016
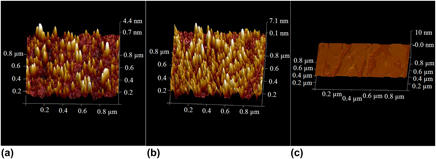
Potassium titanyl phosphate crystals in both x-cut and z-cut were irradiated with 185 MeV Au ions. The morphology of the resulting ion tracks was investigated using small angle x-ray scattering (SAXS), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and atomic force microscopy (AFM). SAXS measurements indicate the presence of cylindrical ion tracks with abrupt boundaries and a density contrast of 1 ± 0.5% compared to the surrounding matrix, consistent with amorphous tracks. The track radius depends on the crystalline orientation, with 6.0 ± 0.1 nm measured for ion tracks along the x-axis and 6.3 ± 0.1 nm for those along the z-axis. TEM images in both cross-section and plan-view show amorphous ion tracks with radii comparable to those determined from SAXS analysis. The protruding hillocks covering the sample surface detected by AFM are consistent with a lower density of the amorphous material within the ion tracks compared to the surrounding matrix. Simulations using an inelastic thermal-spike model indicate that differences in the thermal conductivity along the z- and x-axis can partially explain the different track radii along these directions.