Article contents
Oxidation behavior of in situ synthesized (TiB + TiC)/Ti–6Al–4V composites from Ti–B4C–C and Ti–TiB2–TiC systems
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 19 March 2019
Abstract
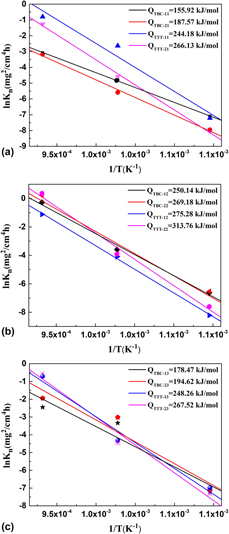
The oxidation behavior of two percentages of TiB + TiC reinforced Ti–6Al–4V composites derived from Ti–B4C–C and Ti–TiB2–TiC systems was investigated at 873–1073 K for 320 h in air. The oxidation weight gain curves of the (TiB + TiC)/Ti–6Al–4V composites at 973 K basically obey parabolic law, while those at 873 and 1073 K mainly follow linear law and parabolic-linear law, respectively. The oxide layers of the composites are predominately found to be rutile TiO2, Al2O3, and the mixture of V2O3 and V2O5. The oxidation layers turn thinner with increasing the nominal volume fraction of reinforcements in the (TiB + TiC)/Ti–6Al–4V composites. Moreover, according to the calculation results of reaction index (n) and effective activation energy (Qeff) and the analyses of cross-sections of the oxidation layers, the oxidation resistance ability of the composites from Ti–TiB2–TiC system is higher than that from Ti–B4C–C system while employing the same sintering temperature and nominal volume fraction of reinforcement.
Information
- Type
- Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2019
References
- 3
- Cited by

