Published online by Cambridge University Press: 25 October 2017
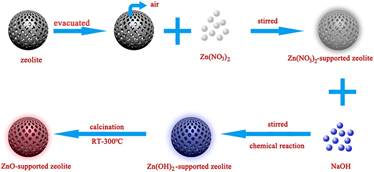
To improve the antimicrobial properties of ZnO, ZnO-supported 13X zeolite (X-ZnO) was prepared via the facile chemical method. Antimicrobial activities of X-ZnO and ZnO were tested against Gram-negative (Escherichia coli) and Gram-positive (Staphylococcus aureus) bacteria. X-ZnO showed noticeable antimicrobial activities against E. coli and S. aureus under visible light conditions, especially against E. coli. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of X-ZnO against E. coli was 0.12–0.24 mg/mL. However, there were still much bacteria alive in the nano-ZnO suspensions at the same concentration. To elucidate the antimicrobial activities of X-ZnO, the average concentration of the total reactive oxygen species (ROS) and Zn2+ ions released from X-ZnO and nano-ZnO were quantitatively analyzed. The obtained results indicated that the average concentration of ROS produced by supported ZnO was much higher than that of nano-ZnO. And the released Zn2+ ions from X-ZnO and nano-ZnO suspensions were much lower than the MIC of Zn2+. Thus, it is believed that the production of ROS in X-ZnO and nano-ZnO suspensions resulted in the difference of antibacterial activities.
Contributing Editor: Lakshmi Nair