Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 March 2012
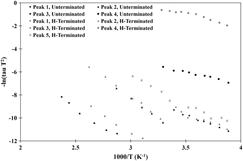
A single crystal aluminum nitride (AlN) wafer surface was investigated via the use of a novel software-based, Charge-based Deep Level Transient Spectroscopy (Q-DLTS) apparatus, both before and after surface bond termination with hydrogen plasma. The sample was cleaned and metalized with a thermoresistive evaporator to create electrical contacts and then annealed in a helium atmosphere at 825 °C. Current-voltage (I-V) measurements were performed to investigate the nature of the metal/substrate contacts. The effect of hydrogen termination was investigated and Arrhenius plots were produced from Q-DLTS spectra at temperatures ranging from −15.9 °C to 136.0 °C. Activation energies and capture cross-section values were calculated from the Q-DLTS spectra for traps existing in the AlN substrate surface. Prior to hydrogen termination, four charge traps were observed with activation energies of 0.31 eV, 0.61 eV, 0.56 eV, and 0.18 eV and capture cross sections 5.6 × 10−21 cm2, 1.1 × 10−16 cm2, 3.5 × 10−19 cm2, and 1.3 × 10−21 cm2, respectively After hydrogen termination, five charge traps were observed with activation energies of 0.31 eV, 0.61 eV, 0.52 eV, 0.19 eV, and 0.40 eV, and capture cross sections 4.9 × 10−21 cm2, 1.3 × 10−16 cm2, 2.9 × 10−19 cm2, 3.1 × 10−19 cm2, and 4.7 × 10−19 cm2, respectively. Four of these peaks after termination are matched with the peaks prior to termination and the fifth peak appears to be the result of the hydrogen termination.