Article contents
Residual stress analysis with stress-dependent growth rate and creep deformation during oxidation
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 22 July 2016
Abstract
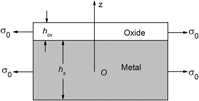
In this paper, taking into account the external loading, growth strain, creep, and bending deformation during the metallic high-temperature oxidation, a residual stress evolution model is developed according to the force- and moment-equilibrium equations. In this model, oxidation kinetic relationship (the stress-dependent growth rate) is related to the stress in the oxide scale, not classical parabolic law. If and only if the stress in the scale or the activation volume is equal to zero, this relationship can reduce to the parabolic law. Then the stress-dependent oxidation kinetics is compared with the stress-independent one (the parabolic law). Finally, effects of the external loading on the stress distribution in the oxide scale, the curvature of the system and the scale thickness are discussed, and numerical results show that the tensile external loading decreases the oxidation stress and promotes the growth rate of the oxidation layer.
Keywords
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2016
References
REFERENCES
- 5
- Cited by



