Article contents
Synthesis of novel core–shell structural AuNR@MCM-41 for infrared light-driven release of drug
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 September 2011
Abstract
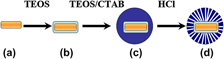
The hexagonal mesoporous silica MCM-41 nanospheres with Au nanorods (AuNRs) as core have been synthesized via a modified Stöber method by a process of hydration and condensation of tetraethoxysilane in a water–ethanol mixture. The AuNR@MCM-41 nanocomposites combine the photothermal characteristic with the mesopore of MCM-41 in one body. We utilized these core–shell materials for ibuprofen encapsulation and release in the simulated body fluid (pH 7.4) for the first time. The results certificated AuNR@MCM-41 nanocomposites as novel dual-functional materials could realize the light-driven release of drug due to the photothermal effect of the AuNRs. Such novel nanomaterials offer a new way for cancer treatment which combine hyperthermia with the chemotherapeutic drugs by synergistic effect.
Keywords
Information
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2011
References
REFERENCES
- 6
- Cited by

