Article contents
Thermal annealing influence on structural, magnetic, electronic, and mechanical properties of off-stoichiometric Ni40Cu10Mn35Ti15 all-d-metal Heusler alloy
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 August 2020
Abstract
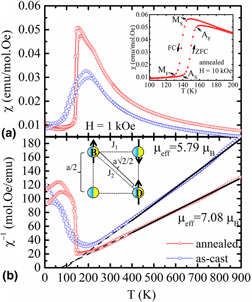
We have synthesized off-stoichiometric Ni40Cu10Mn35Ti15 all-d-metal Heusler alloy with a B2 cubic crystal structure by an arc melting process and investigated its structural, magnetic, electronic, thermal, and mechanical properties under the influence of a single-step thermal annealing. The compound exhibits an antiferromagnetic ordering accompanied by thermal hysteresis indicating a first-order magneto-structural transition. Curie–Weiss molecular field analysis reveals the presence of ferromagnetic interactions competing with long-range antiferromagnetic ordering. Thermal annealing leads to the appearance of a heat capacity sharp peak around antiferromagnetic transition. Electrical resistivity measurements display abrupt changes close to the magneto-structural transition revealing the strong coupling among spin, lattice, and charge degrees of freedom characteristic of a martensitic transition (MT). We have also evaluated its mechanical properties from microhardness measurements, and the results indicate that this alloy exhibits ductile behavior. The occurrence of MT associated with improved ductility is an essential combination for technological application as shape-memory alloys.
Keywords
- Type
- Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Author(s), 2020, published on behalf of Materials Research Society by Cambridge University Press
References
- 11
- Cited by



