Published online by Cambridge University Press: 09 November 2018
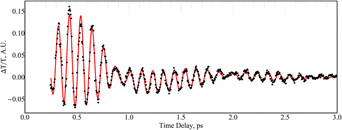
Transient transmission oscillations in X-cut and Z-cut congruent, iron-doped, and magnesium-doped lithium niobate samples were measured using 50 fs, 800 nm, 0.5 nJ pulses from a self-mode-locked Ti:sapphire laser in an optical pump–probe system. Several Raman-active oscillation modes excited by these pulses were observed as changes in the transmitted probe intensity versus time delay between the pump and probe pulses. The samples were rotated to determine how the incident polarization of the pump pulses affects the mode excitations. The observed Raman-active oscillations correspond to previously reported symmetry modes measured with traditional, continuous-wave, Raman spectroscopy using the same scattering geometry. In addition, a polariton mode and other, previously unreported, lower-frequency modes were observed in each of the samples. The transmission intensity data for each sample were fit successfully to a superposition of sinusoidal functions with exponentially decaying amplitudes.