Article contents
Ultrafiltration performance and fouling resistance of PVB/SPES blend membranes with different degree of sulfonation
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 18 August 2015
Abstract
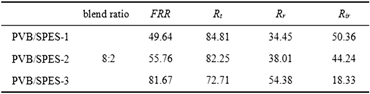
In the present study, we investigated the effects of different degree of sulfonation (DS) on the performance of the poly (vinyl butyral)/sulfonated polyethersulfone (PVB/SPES) blend membranes. The compatibility of the PVB/SPES blending system was characterized by shear viscosity and Fourier transform infrared attenuated total reflection, respectively. Results stated that all PVB/SPES blending systems were partially compatible. Contact angle, equilibrium water content, and x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy measurements were carried out to investigate the hydrophilicity of the PVB/SPES blend membranes. With increasing DS, the blend membranes became more hydrophilic. The pure water flux of the blend membranes increased with DS, while the rejection decreased due to microstructures of the PVB/SPES membranes. The mechanical properties of the PVB/SPES blend membranes increased slightly with DS. Fouling resistances of blend membranes evaluated by bovine serum albumin solution filtration revealed the PVB/SPES blend membranes with DS = 27% exhibited the superior antifouling properties.
Information
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2015
References
REFERENCES
- 2
- Cited by

