No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 31 January 2011
X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Raman spectroscopy have been used for the study of the bi-intercalation of SbCl5 into a stage 5 FeCl3-graphite intercalation compound (GIC). The stage 5 FeCl3-GIC is prepared by an ordinary two-bulb method with the temperature of graphite at 788 K and that of FeCl3 at 573 K. The FeCl3-SbCl5-graphite bi-intercalation compound (GBC) with one SbCl5 layer is obtained when the temperature of the stage 5 FeCl3-GIC is held at 443 K and the temperature of SbCl5 at 373 K in the two-zone system. The stacking sequence of the GBC is found to be an admixture of G(FeCl3)GG(SbCl5)GGG(FeCl3)G and G(FeCl3)GGG(SbCl5)GG(FeCl3)G by XRD, where G, (FeCl3), and (SbCl5) are the graphite, FeCl3, and SbCl5 layers, respectively. The Raman spectrum of the GBC shows two peaks associated with the 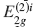 and
and 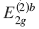 modes at 1588 cm−1 and 1610 cm−1, respectively. For the temperatures of stage 5 FeCl3-GIC at 443 K and SbCl5 at 403 K in the two-zone system, the FeCl3-SbCl5-GBC with two SbCl5 layers is obtained. The stacking sequence of the GBC is determined to be an admixture of G(FeCl3)GG(SbCl5)GG(SbCl5)G(FeCl3)G and G(FeCl3)G(SbCl5)GG(SbCl5)GG(FeCl3)G In the Raman spectrum of this GBC, two peaks associated with the
modes at 1588 cm−1 and 1610 cm−1, respectively. For the temperatures of stage 5 FeCl3-GIC at 443 K and SbCl5 at 403 K in the two-zone system, the FeCl3-SbCl5-GBC with two SbCl5 layers is obtained. The stacking sequence of the GBC is determined to be an admixture of G(FeCl3)GG(SbCl5)GG(SbCl5)G(FeCl3)G and G(FeCl3)G(SbCl5)GG(SbCl5)GG(FeCl3)G In the Raman spectrum of this GBC, two peaks associated with the 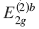 mode are observed at 1616 and 1624 cm−1.
mode are observed at 1616 and 1624 cm−1.