Article contents
Convective plasma transport modelled with propagators
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 March 2009
Abstract
The transport of plasma under the influence of a significant flow velocity in a toroidal stellarator has been modelled using an efficient numerical scheme based on ‘propagators’. The particle density has been calculated in a poloidal cross-section from the fluid particle conservation equation, using a flow velocity and a diffusion coefficient derived from experimentally obtained values. The formation of hollow density profiles during ECH has been examined, by varying the flow velocity v(r,θ) of the bulk of the plasma while ensuring that 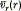 (its component in the minor-radial direction, averaged over poloidal angle θ) is consistent with experiment. A radial flow
(its component in the minor-radial direction, averaged over poloidal angle θ) is consistent with experiment. A radial flow 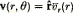 does not seem to account for the very hollow profiles observed in experiment. Hollownesses of between 1·5 and 5 were obtained for other plausible forms of v(r, θ).
does not seem to account for the very hollow profiles observed in experiment. Hollownesses of between 1·5 and 5 were obtained for other plausible forms of v(r, θ).
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Cambridge University Press 1989
References
REFERENCES
- 5
- Cited by


