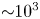1 Introduction: free electron laser in astrophysical setting
Pulsars’ radio emission mechanism(s) eluded identification for nearly half a century (e.g. Melrose Reference Melrose2000; Lyubarsky Reference Lyubarsky2008; Eilek & Hankins Reference Eilek and Hankins2016). Most likely, several types of coherent processes operate in different sources (e.g. magnetars versus pulsars) and in different parts of pulsar magnetospheres (see, e.g. the discussion in Lyutikov, Burzawa & Popov Reference Lyutikov, Burzawa and Popov2016).
The problem of pulsar coherent emission generation has been brought back to the research forefront by the meteoritic developments over the last years in the field of mysterious fast radio bursts (FRBs). Especially important was the detection of a radio burst from a galactic magnetar by CHIME and STARE2 collaborations in coincidence with high energy bursts (Andersen et al. Reference Andersen, Bandura, Bhardwaj, Bij, Boyce, Boyle, Brar, Cassanelli and Chawla2020; Bochenek et al. Reference Bochenek, Ravi, Belov, Hallinan, Kocz, Kulkarni and McKenna2020; Mereghetti et al. Reference Mereghetti, Savchenko, Ferrigno, Götz, Rigoselli, Tiengo, Bazzano, Bozzo, Coleiro and Courvoisier2020; Li et al. Reference Li, Lin, Xiong, Ge, Li, Li, Lu, Zhang, Tuo and Nang2021; Ridnaia et al. Reference Ridnaia, Svinkin, Frederiks, Bykov, Popov, Aptekar, Golenetskii, Lysenko, Tsvetkova and Ulanov2021). The similarity of properties of magnetars’ bursts to the FRBs gives credence to the magnetar origin of FRBs (even though the radio powers are quite different – there is a broad distribution).
The phenomenon of FRBs challenges our understating of relativistic plasma coherent processes to the extreme. In this case radio waves can indeed carry an astrophysically important amount of the energy. For example, radio luminosity in FRBs can match, for a short period of time, the macroscopic Eddington luminosity and exceed total solar luminosity by many orders of magnitude. Still, the fraction emitted in radio remains small – this relatively small fraction of total energy that pulsars and FRBs emit in radio (${\sim }10^{-5}$![]() is typical) is theoretically challenging: simple order-of-magnitude estimates cannot be used. Emission production and saturation levels of instabilities depend on the kinetic details of the plasma distribution function.
is typical) is theoretically challenging: simple order-of-magnitude estimates cannot be used. Emission production and saturation levels of instabilities depend on the kinetic details of the plasma distribution function.
Lyutikov (Reference Lyutikov2021) developed a model of the generation of coherent radio emission in the Crab pulsar, magnetars and FRBs due to a variant of the free electron laser (FEL) mechanism, operating in a weakly turbulent, guide-field dominated plasma. This presents a new previously unexplored way (in astrophysical settings) of producing coherent emission via parametric instability.
A particular regime of the FEL (SASE – self-amplified spontaneous emission) micro-bunching is initiated by the spontaneous radiation. In the beam frame the wiggler and the electromagnetic (EM) wave have the same frequency/wavenumber, but propagate in the opposite direction. The addition of two counter-propagating waves creates a standing wave in the beam frame. The radiation energy density is smaller at the nodes of the standing wave: this creates a ponderomotive force that pushes the particles towards the nodes – bunches are created. These bunches are still shaken by the electromagnetic wiggler: they emit in phase, coherently.
Somewhat surprisingly, the FEL model in magnetically dominated regimes (Lyutikov Reference Lyutikov2021) is both robust to the underlying plasma parameters and succeeded in reproducing the following observed features. (i) Emission frequencies depend mostly on the scale of turbulent fluctuations and the Lorentz factor of the reconnection-generated beam, (2.5); it is independent of the absolute value of the underlying magnetic field. (ii) The model explained both broadband emission and the presence of emission stripes, including multiple stripes observed in the high frequency interpulse of the Crab pulsar. (iii) The model reproduced correlated spectrum-polarization properties: the presence of narrow emission bands in the spectrum favours linear polarization, while broadband emission can have arbitrary polarization. The model is applicable to a very broad range of neutron star parameters: the model is mostly independent of the value of the magnetic field. It is thus applicable to a broad variety of neutron stars (NSs), from fast spin/weak magnetic field millisecond pulsars to slow spin/supercritical magnetic field in magnetars, and from regions near the surface up to (and a bit beyond of) the light cylinder.
The guide-field dominance plays a tricky role in the operation of an FEL. On the one hand it suppresses the growth rate, but what turns out to be more important in astrophysical applications is that the guide-field dominance helps to maintain beam coherence. Without the guide field, particles with different energies follow different trajectories in the magnetic field of the wiggler, and quickly lose coherence even for a small initial velocity spread. In contrast, in the guide-field dominated regime all particles follow, basically, the same trajectory. Hence, coherence is maintained as long as the velocity spread in the beam frame is $\Delta \beta \leq 1$![]() . Such tolerance to velocity spread is an unusual property of a guide-field dominated FEL.
. Such tolerance to velocity spread is an unusual property of a guide-field dominated FEL.
2 A FEL in the guide-field dominated regime: theoretical summary
2.1 Model parameters
Let us next discuss the basic model parameters. (Unfortunately, there is some confusion in standard definitions used in literature.)
The model starts with an assumption that guiding magnetic field lines are perturbed by a packet of linearly polarized Alfvén waves of intensity $B_w$![]() and frequency $\omega$
and frequency $\omega$![]() . In highly magnetized force-free plasma Alfvén waves propagating along the magnetic field are nearly luminal, $v_A \approx c$
. In highly magnetized force-free plasma Alfvén waves propagating along the magnetic field are nearly luminal, $v_A \approx c$![]() .
.
The first parameter is dimensionless wave intensity. We chose notation $a_0$![]() , which is standard in the laser community and sometimes used in the FEL community as well,
, which is standard in the laser community and sometimes used in the FEL community as well,
It should be remarked that in the FEL literature parameters $K$![]() and $a_0$
and $a_0$![]() are often used interchangeably. In this paper we follow the nomenclature used for $K$
are often used interchangeably. In this paper we follow the nomenclature used for $K$![]() in (2.4) below in Jackson (Reference Jackson1975, paragraph 14.7)
in (2.4) below in Jackson (Reference Jackson1975, paragraph 14.7)
For the guide-field dominated regime, another parameter is the relative intensity
where $B_0$![]() is a guide field. We assume that the wave is relatively weak, $\delta \ll 1$
is a guide field. We assume that the wave is relatively weak, $\delta \ll 1$![]() .
.
A (reconnection-generated) beam of particles with Lorentz factor $\gamma _b$![]() propagates along the rippled magnetic field in a direction opposite to the direction of the Alfvén waves. In the frame of the beam the waves are seen with $k_{w}'= 2 \gamma _b k_{w}$
propagates along the rippled magnetic field in a direction opposite to the direction of the Alfvén waves. In the frame of the beam the waves are seen with $k_{w}'= 2 \gamma _b k_{w}$![]() . In the guide-field dominated regime the cyclotron frequency associated with the guide field is much larger than the frequency of the wave in the beam frame, and the cyclotron frequency associated with the fluctuating field; hence,
. In the guide-field dominated regime the cyclotron frequency associated with the guide field is much larger than the frequency of the wave in the beam frame, and the cyclotron frequency associated with the fluctuating field; hence,
where $\varOmega _0 = e B_0/(m_e c)$![]() is the cyclotron frequency (non-relativistic) of the guide field and $\varOmega _w = e B_w/(m_e c)$
is the cyclotron frequency (non-relativistic) of the guide field and $\varOmega _w = e B_w/(m_e c)$![]() is the cyclotron frequency associated with the wiggler field.
is the cyclotron frequency associated with the wiggler field.
Another important parameter, defined by Jackson (Reference Jackson1975, paragraph 14.7), is the wiggler-undulator parameter
This parameter is related to the magnitude of the wiggler-induced oscillations in the beam trajectory, which is also related to the opening angle of the cone of the generated radiation. When $K \gg 1$![]() , this oscillation is large and the pump field is sometimes referred to as a ‘wiggler’. In the opposite regime where $K \ll 1$
, this oscillation is large and the pump field is sometimes referred to as a ‘wiggler’. In the opposite regime where $K \ll 1$![]() the pump field is sometimes referred to as an ‘undulator’. In this paper we will refer to the pump field as a wiggler throughout.
the pump field is sometimes referred to as an ‘undulator’. In this paper we will refer to the pump field as a wiggler throughout.
The $K$![]() parameter (2.4) is a product of two quantities, relative amplitude $\delta \ll 1$
parameter (2.4) is a product of two quantities, relative amplitude $\delta \ll 1$![]() and Lorentz factor $\gamma _ b \gg 1$
and Lorentz factor $\gamma _ b \gg 1$![]() , so generally its values can be either large or small. A relativistically moving electron emits in a cone with opening angle $\Delta \theta \sim 1/\gamma$
, so generally its values can be either large or small. A relativistically moving electron emits in a cone with opening angle $\Delta \theta \sim 1/\gamma$![]() . In the $K \ll 1$
. In the $K \ll 1$![]() regime that opening angle is much larger than the variation in the bulk direction of emission at different points in the trajectory; see figure 1, left panel. The radiation detected by an observer is an almost coherent superposition of the contributions from all the oscillations in the trajectory at a frequency
regime that opening angle is much larger than the variation in the bulk direction of emission at different points in the trajectory; see figure 1, left panel. The radiation detected by an observer is an almost coherent superposition of the contributions from all the oscillations in the trajectory at a frequency
We note that the axial velocity in the strong axial guide-field regime is nearly constant and close to the speed of light for high energy electrons; see figure 7 in § 4.3. Hence, the resonant frequency is also nearly constant.

Figure 1. Different regimes of wave–particle interaction depending on the parameter $K$![]() (2.4). Grey cones illustrate the instantaneous emission cone.
(2.4). Grey cones illustrate the instantaneous emission cone.
In the $K\gg 1$![]() regime the variations in the direction of emission are much larger than the angular width of the emission at any point in the trajectory; see figure 1(b). As a result, an observer located within angle $\leq \delta$
regime the variations in the direction of emission are much larger than the angular width of the emission at any point in the trajectory; see figure 1(b). As a result, an observer located within angle $\leq \delta$![]() with respect to the overall guide field see periodic bursts of emission with typical frequency
with respect to the overall guide field see periodic bursts of emission with typical frequency
Since $K \gg 1$![]() in this regime, the resulting frequency is higher than that for the case where $K \ll 1$
in this regime, the resulting frequency is higher than that for the case where $K \ll 1$![]() . In this paper we work in the $K \ll 1$
. In this paper we work in the $K \ll 1$![]() regime, which is the regime more typical of FELs.
regime, which is the regime more typical of FELs.
Another terminology issue: here we contrast the term ‘Compton’ with ‘curvature’, not with ‘Raman’ regime, which is Compton-like scattering, but on collective plasma fluctuations.
In this paper we work in the regime $K \ll 1$![]() (this is the usual regime of FELs). The scattered frequency is then given by (2.5); below we drop the subscript $C$
(this is the usual regime of FELs). The scattered frequency is then given by (2.5); below we drop the subscript $C$![]() .
.
2.2 Overview of main results of Lyutikov (Reference Lyutikov2021)
Lyutikov (Reference Lyutikov2021) developed a model of the generation of coherent radio emission in the Crab pulsar, magnetars and FRBs whereby the emission is produced by a reconnection-generated beam of particles via a variant of the FEL mechanism, operating in a weakly turbulent, guide-field dominated plasma. The guide-field dominance is a key new feature that distinguishes this regime from the conventional laboratory FELs: a (reconnection-generated) beam of particles with Lorentz factor $\gamma _b$![]() propagates along the wiggled magnetic field in a direction opposite to the direction of the Alfvén waves. In the frame of the beam the waves are seen with $k_{w,b}= 2 \gamma _b k_{w}$
propagates along the wiggled magnetic field in a direction opposite to the direction of the Alfvén waves. In the frame of the beam the waves are seen with $k_{w,b}= 2 \gamma _b k_{w}$![]() . Guide-field dominance requires $2 \gamma _b k_{w} c \ll \varOmega _0$
. Guide-field dominance requires $2 \gamma _b k_{w} c \ll \varOmega _0$![]() .
.
The key results of Lyutikov (Reference Lyutikov2021) are as follows.Footnote 1
(i) The interaction Hamiltonian (this is particularly important for the present work, as it describes evolution of the instability and its saturation). Particle motion in the combined fields of the wiggler $B_w$
 , the EM wave $E_{EM}$
, the EM wave $E_{EM}$ (both with wave vector $k_{w}'$
(both with wave vector $k_{w}'$ in the beam frame) and the guide field $B_0 \gg E_w, E_{EM}$
in the beam frame) and the guide field $B_0 \gg E_w, E_{EM}$ can be described by a simple ponderomotive Hamiltonian (Lyutikov Reference Lyutikov2021, (39))
(2.7)\begin{equation} {\mathcal{H}} = \frac{\beta_z^2}{2} + \delta \left(\frac{ E_{EM}}{B_0} \right) \left( \frac{\varOmega_0}{ k_w c} \right) \sin ^2( k_{w}' z), \end{equation}where $\beta _z$
can be described by a simple ponderomotive Hamiltonian (Lyutikov Reference Lyutikov2021, (39))
(2.7)\begin{equation} {\mathcal{H}} = \frac{\beta_z^2}{2} + \delta \left(\frac{ E_{EM}}{B_0} \right) \left( \frac{\varOmega_0}{ k_w c} \right) \sin ^2( k_{w}' z), \end{equation}where $\beta _z$
 is axial velocity; see figure 2. The second term is the ponderomotive potential. The Hamiltonian formulation allows powerful analytical methods to be applied to the system (adiabatic invariant, phase space separatrix etc). This is especially important for the estimates of the nonlinear saturation, one of the main goals of the present work.
is axial velocity; see figure 2. The second term is the ponderomotive potential. The Hamiltonian formulation allows powerful analytical methods to be applied to the system (adiabatic invariant, phase space separatrix etc). This is especially important for the estimates of the nonlinear saturation, one of the main goals of the present work.(ii) The growth rate of the parametric instability is (Lyutikov Reference Lyutikov2021, (62))
(2.8)\begin{equation} \varGamma = \left( \left( \frac{ E_w}{B_0} \right) \left( \frac{ E_{EM}}{B_0} \right) {\varOmega_0}{ k_w c} \right)^{1/2} \propto B_0^{{-}1/2}. \end{equation}Importantly, it is only mildly suppressed by the strong guide field.
(iii) Saturation level. The ponderomotive potential increases linearly with EM wave intensity, while energy density of EM waves increases quadratically. The corresponding saturated velocity jitter (Lyutikov Reference Lyutikov2021, (73))
(2.9)\begin{equation} \beta_{S} = \frac{\delta}{ \sqrt{2 \gamma}} \frac{\omega_p}{k_w c} \end{equation}
(iv) The guide-field dominance plays a dual role. First, it reduces the growth rate, but only mildly, ${\propto } B_0^{-1/2}$
 (2.8). What is more important, the strong guide field helps to maintain beam coherence. Without the guide field, particles with different energies follow different trajectories and quickly lose coherence even for a small initial velocity spread. In contrast, in the guide-field dominated regime all particles follow, basically, the same trajectory. Hence, coherence is maintained as long as the velocity spread in the beam frame is $\Delta \beta \leq 1$
(2.8). What is more important, the strong guide field helps to maintain beam coherence. Without the guide field, particles with different energies follow different trajectories and quickly lose coherence even for a small initial velocity spread. In contrast, in the guide-field dominated regime all particles follow, basically, the same trajectory. Hence, coherence is maintained as long as the velocity spread in the beam frame is $\Delta \beta \leq 1$ (see figure 13 of Lyutikov Reference Lyutikov2021). As a result, the model requires only a mildly narrow distribution of the beam's particles, $\Delta p /p_0 \leq 1$
(see figure 13 of Lyutikov Reference Lyutikov2021). As a result, the model requires only a mildly narrow distribution of the beam's particles, $\Delta p /p_0 \leq 1$ and the spectrum of turbulence $\Delta k_{w,b}/k_{w,b} \leq 1$
and the spectrum of turbulence $\Delta k_{w,b}/k_{w,b} \leq 1$
(v) The model operates in a very broad range of the neutron star's parameters: the model is independent of the value of the magnetic field. It is thus applicable to a broad variety of NSs, from fast spin/weak magnetic field millisecond pulsars to a slow spin/supercritical magnetic field in magnetars, and from regions near the surface up to (and a bit beyond of) the light cylinder.

Figure 2. Particle dynamics for FEL in the guide-field dominated plasma with the ponderomotive potential (2.7) (arbitrary unites chosen to illustrate the trajectory Lyutikov Reference Lyutikov2021). (a) Three-dimensional rendering of particle trajectories in the beam frame (a particle experiences a saddle-like trajectory). (b) Trajectory of trapped particles in phase $\beta _z$![]() –$z$
–$z$![]() plane; velocity is normalized to the separatrix $\beta _{S}$
plane; velocity is normalized to the separatrix $\beta _{S}$![]() (2.9).
(2.9).
3 Simulations with ONEDFEL codes
3.1 The codes
In this work we performed simulations of the interaction of a single-charged relativistic beam with the wiggler using the FEL code ONEDFEL (Freund & Antonsen Reference Freund and Antonsen2024). ONEDFEL is a time-dependent code that simulates the FEL interaction in one dimension. The radiation fields are tracked by integration of the wave equation under the slowly varying envelope approximation. As such, the wave equation is averaged over the fast time scale under the assumption that the wave amplitudes vary slowly over a wave period. The dynamical equations are a system of ordinary differential equations for the mode amplitudes of the field and the Lorentz force equations for the electrons that are integrated simultaneously using a fourth order Runge–Kutta algorithm. Time dependence is treated by including multiple temporal ‘slices’ in the simulation that are separated by an integer number of wavelengths. The numerical procedure is that each slice is advanced from $z \to z + \Delta z$![]() separately by means of the Runge–Kutta algorithm. Time dependence is imposed as an additional operation by using the forward time derivative as an additional source term to treat the slippage of the radiation field with respect to the electrons. Slippage occurs at the rate of one wavelength per undulator period in the low gain regime and after saturation of the high gain regime but at the rate of one third of a wavelength per undulator period in the exponential gain regime (Bonifacio et al. Reference Bonifacio, Casagrande, Cerchioni, Salvo Souza, Pierini and Piovella1990; Saldin, Schneidmiller & Yurkov Reference Saldin, Schneidmiller and Yurkov1995; Freund & Antonsen Reference Freund and Antonsen2024). ONEDFEL self-consistently describes slippage in each of these regimes. The simplest way to accomplish this is to use a linear interpolation algorithm to advance the field from the $(i -1)$
separately by means of the Runge–Kutta algorithm. Time dependence is imposed as an additional operation by using the forward time derivative as an additional source term to treat the slippage of the radiation field with respect to the electrons. Slippage occurs at the rate of one wavelength per undulator period in the low gain regime and after saturation of the high gain regime but at the rate of one third of a wavelength per undulator period in the exponential gain regime (Bonifacio et al. Reference Bonifacio, Casagrande, Cerchioni, Salvo Souza, Pierini and Piovella1990; Saldin, Schneidmiller & Yurkov Reference Saldin, Schneidmiller and Yurkov1995; Freund & Antonsen Reference Freund and Antonsen2024). ONEDFEL self-consistently describes slippage in each of these regimes. The simplest way to accomplish this is to use a linear interpolation algorithm to advance the field from the $(i -1)$![]() th slice to the $i$
th slice to the $i$![]() th slice. Using this procedure ONEDFEL can treat electron beams and radiation fields with arbitrary temporal profiles and it is possible to simulate complex spectral properties.
th slice. Using this procedure ONEDFEL can treat electron beams and radiation fields with arbitrary temporal profiles and it is possible to simulate complex spectral properties.
Simulations, effectively, work in the lab frame, The general set-up consists of the following.
(i) Guide magnetic field $B_0$
 (as strong as numerically possible).
(as strong as numerically possible).(ii) A wiggler with wavenumber $k_w$
 and relative amplitude $\delta = B_w/B_0 \ll 1$
and relative amplitude $\delta = B_w/B_0 \ll 1$ is as EM wave (with adiabatic turning on); wiggler's frequency in the beam frame is below the cyclotron frequency associated with the guide field, $\omega _w \sim \gamma _b \ll \omega _{B_0}$
is as EM wave (with adiabatic turning on); wiggler's frequency in the beam frame is below the cyclotron frequency associated with the guide field, $\omega _w \sim \gamma _b \ll \omega _{B_0}$ (but can be comparable to the cyclotron frequency of the wiggler, $\omega _{B_w}$
(but can be comparable to the cyclotron frequency of the wiggler, $\omega _{B_w}$ ).
).(iii) A charged beam with a ‘solid’ (dead) neutralizing background; the corresponding Alfvén wave is relativistic, $v_A \sim c$
 . The beam is initially propagating along the magnetic field (no gyration).
. The beam is initially propagating along the magnetic field (no gyration).(iv) The pulse duration is much longer than the wiggler wavelength.
By using a pure EM wave, and not as a self-consistent Alfvén wave, eliminates complications related to setting the correct particle currents. In the highly magnetized regime $\sigma \gg 1$![]() , Alfvén waves are nearly luminal (here $\sigma = B^2/(4{\rm \pi} \rho c^2)$
, Alfvén waves are nearly luminal (here $\sigma = B^2/(4{\rm \pi} \rho c^2)$![]() is the magnetization parameter (Kennel & Coroniti Reference Kennel and Coroniti1984)).
is the magnetization parameter (Kennel & Coroniti Reference Kennel and Coroniti1984)).
Let us next comment on the applicability of the one-dimensional regime. The post-eruption magnetic field lines are mostly radial. Development of a coronal mass ejection (CME), accompanying magnetospheric FRBs, leads to opening of the magnetosphere from radii $R_0$![]() , much smaller than the light cylinder (Sharma, Barkov & Lyutikov Reference Sharma, Barkov and Lyutikov2023); see figure 3. After the generation of a CME the magnetosphere becomes open, with nearly radial magnetic field lines for $r\geq R_O$
, much smaller than the light cylinder (Sharma, Barkov & Lyutikov Reference Sharma, Barkov and Lyutikov2023); see figure 3. After the generation of a CME the magnetosphere becomes open, with nearly radial magnetic field lines for $r\geq R_O$![]()

Figure 3. Post-flare opening of the magnetosphere (Sharma et al. Reference Sharma, Barkov and Lyutikov2023). Colour represent values of $r \sin \theta B_{\phi }$![]() and lines are poloidal field lines. The spin parameter is $\varOmega =0.2$
and lines are poloidal field lines. The spin parameter is $\varOmega =0.2$![]() , so that before the ejection of a CME the light cylinder is at $R_{LC} =5$
, so that before the ejection of a CME the light cylinder is at $R_{LC} =5$![]() (the dashed white line is the last closed magnetic field). Post-flare magnetosphere is open, starting $R_O \ll R_{LC}$
(the dashed white line is the last closed magnetic field). Post-flare magnetosphere is open, starting $R_O \ll R_{LC}$![]() . At $r \geq R_O$
. At $r \geq R_O$![]() the magnetosphere has a monopolar-like magnetic field structure. The appearance of the plasmoids (‘ejected plasmoid’) is not important for the present work.
the magnetosphere has a monopolar-like magnetic field structure. The appearance of the plasmoids (‘ejected plasmoid’) is not important for the present work.
4 Results
In simulating the magnetar magnetosphere environment we consider an electron beam propagating along the magnetic field in the presence of a plane-polarized electromagnetic wave. The basic parameters are shown in table 1. We consider a mono-energetic 50 MeV beam over a bunch length/charge of $1.8\,\mathrm {\mu }$![]() s/5.9 mC with a peak current of 5 kA. The beam plasma frequency corresponding to a 5 kA beam with a radius of 100 cm is about 1.6 kHz. The electromagnetic undulator is taken to have a period of 100 m and an amplitude of 0.01 kG. The excited radiation therefore is also plane polarized. We study the interaction for various values of the axial field so that the resonant wavelength will vary with the axial field.
s/5.9 mC with a peak current of 5 kA. The beam plasma frequency corresponding to a 5 kA beam with a radius of 100 cm is about 1.6 kHz. The electromagnetic undulator is taken to have a period of 100 m and an amplitude of 0.01 kG. The excited radiation therefore is also plane polarized. We study the interaction for various values of the axial field so that the resonant wavelength will vary with the axial field.
Table 1. Parameters of simulations.

The parameters of simulations nearly match the real physical condition (except the value of the guide field): for a beam Lorentz factor $\gamma _b \sim 100$![]() and a wiggler length $\lambda _w \sim 100$
and a wiggler length $\lambda _w \sim 100$![]() m, the resonant wavelength is a few centimetres. These values are close to the real scales we expect in neutron star magnetospheres. As mentioned previously, the guide field is below that expected but the numerical simulation becomes more and more computationally challenging as the resonant linewidth becomes narrower for high guide fields. However, the wavelength becomes independent of the guide field (figure 4). In this particular example, over a few kilometres (also a realistic physical value) the intensity grows by fourteen orders of magnitude and reaches saturation.
m, the resonant wavelength is a few centimetres. These values are close to the real scales we expect in neutron star magnetospheres. As mentioned previously, the guide field is below that expected but the numerical simulation becomes more and more computationally challenging as the resonant linewidth becomes narrower for high guide fields. However, the wavelength becomes independent of the guide field (figure 4). In this particular example, over a few kilometres (also a realistic physical value) the intensity grows by fourteen orders of magnitude and reaches saturation.

Figure 4. Steady-state runs. (a) Variation in the FEL resonant wavelength with the magnetic field in the group II regime. (b) The saturated power and saturation distance versus wavelength for $B_0 = 0.2$![]() kG.
kG.
4.1 Steady-state runs
Using steady-state (i.e. time-independent) ONEDFEL simulations, we have studied the variation in the resonant wavelength with increases in the magnetic field. As shown in figure 4, the resonant wavelength for the FEL interaction decreases from about 0.25 m for a magnetic field of 0.15 kG to 0.053 m when the magnetic field increases to 0.20 kG. We observe that the curve is approaching an asymptote as $B_0$![]() increases past 0.20 kG. This means that the resonant wavelength will remain relatively constant as the magnetic field increases above this value and we expect that the interaction properties will not change significantly for still higher field levels. This is important because simulations become increasing challenging as the field increases beyond this point. Independence of the resonant wavelength on the value of the guide magnetic field is expected; see (2.5).
increases past 0.20 kG. This means that the resonant wavelength will remain relatively constant as the magnetic field increases above this value and we expect that the interaction properties will not change significantly for still higher field levels. This is important because simulations become increasing challenging as the field increases beyond this point. Independence of the resonant wavelength on the value of the guide magnetic field is expected; see (2.5).
The variation in the saturated power and saturation distance (when starting from noise) are shown in figure 4 for $B_0 = 0.20$![]() kG. Here we observe that the full width of the gain band extends from about 0.051 to 0.056 m and the optimal wavelength, corresponding to the shortest saturation distance, is 0.053 m (as indicated in figure 4) and decreases rapidly as the wavelength increases within this gain band
kG. Here we observe that the full width of the gain band extends from about 0.051 to 0.056 m and the optimal wavelength, corresponding to the shortest saturation distance, is 0.053 m (as indicated in figure 4) and decreases rapidly as the wavelength increases within this gain band
4.2 Time-dependent simulations
Next, we ran time-dependent simulations using ONEDFEL. Simulations were conducted to determine the resonant wavelengths for different values of the axial magnetic field. Note that while these are one-dimensional simulations, we need to specify the beam radius in order to determine the current density and beam plasma frequency.
Our results are plotted in figure 5. Importantly, the signal evolves from noise – there is no seeding. The simulations nearly match the real physical condition: for beam Lorentz factor $\gamma \sim 100$![]() and wiggler length $\lambda _w =100$
and wiggler length $\lambda _w =100$![]() m, the resonant wavelength is a few centimetres. These values are close to the real scales we expect in neutron star magnetospheres. The guide field is below that expected though. For high guide fields, the procedure becomes more and more computationally challenging as the resonant line becomes narrower. Over a scale of a few kilometres (also a realistic physical value) the intensity grows by fourteen orders of magnitude, reaching saturation.
m, the resonant wavelength is a few centimetres. These values are close to the real scales we expect in neutron star magnetospheres. The guide field is below that expected though. For high guide fields, the procedure becomes more and more computationally challenging as the resonant line becomes narrower. Over a scale of a few kilometres (also a realistic physical value) the intensity grows by fourteen orders of magnitude, reaching saturation.

Figure 5. The FEL power as a function of distance (over a scale of approximately a few kilometres – realistic neutron star setting). We observe a growth of the EM signal over approximately fourteen orders of magnitude, from noise (no seeding).
The resulting spectral structure is most revealing; see figure 6. We find, first, that there is a typical wavelength of the produced emission (a) – this is a natural consequence of our assumption. We also find that the pulse has a complicated internal spectral structure, (figure 6b) – which is a natural property of a SASE FEL. The spectral width of the central spike is less than 1 % (full width at half maximum). This complicated internal structure resembles what is indeed seen in FRBs (figure 6d). Fast radio bursts display a wide variety of complex time-frequency structures (Ravi et al. Reference Ravi, Shannon, Bailes, Bannister, Bhandari, Bhat, Burke-Spolaor, Caleb, Flynn and Jameson2016; Michilli et al. Reference Michilli, Seymour, Hessels, Spitler, Gajjar, Archibald, Bower, Chatterjee, Cordes and Gourdji2018), including strong modulations in both frequency and time (with a characteristic bandwidth of ${\sim }100$![]() kHz.)
kHz.)

Figure 6. (a,b) Time-dependent simulations of the FEL with ONEDFEL showing a line-like feature (a) with a zoomed-in (b) complicated internal spectral structure of the FEL in the SASE regime. The red line is the averaged spectrum. (c) Distribution of brightest peaks normalized to maximal; (d) dynamic spectrum of FRB150807 (Ravi et al. Reference Ravi, Shannon, Bailes, Bannister, Bhandari, Bhat, Burke-Spolaor, Caleb, Flynn and Jameson2016) showing strong modulations in both frequency and time. (Time and frequency structures are interdependent in the de-dispersion procedures.)
We also attempted a statistical description of the peaks; see figure 6(c). Since we are not aware of any theoretical prediction for the distribution of the peak, we cannot do a proper statistical analysis. Plus, naturally, any particular realization of the peaks is subject to numerous uncertainties, both physical, numerical and statistical.
4.3 Connection to CARM regime
The particle–wave interaction may lead to the excitation of the cyclotron motion and ensuing azimuthal bunching of emitting electrons. This will take us into the cyclotron auto-resonance maser (CARM regime). In this case, the resonant wavelength is governed by the axial velocity of the electron beam and, for fixed beam energy and undulator parameters, this will vary with the axial field. The combination of the wiggler and axial magnetic fields results in particle trajectories that exhibit a magneto-resonance in which the transverse velocity increases as the difference between the wiggler and Larmor periods decreases. The energy corresponding to the transverse velocity cannot exceed the total energy; hence, there are two distinct classes of trajectories corresponding to cases where the Larmor period is longer than the wiggler period (termed group I) and shorter than the wiggler period (termed group II). The variation in the axial velocity, $\beta _\parallel$![]() , as the axial magnetic field increases (for given values of the wiggler period, field strength and electron energy) is illustrated in figure 7 (taken from Freund & Antonsen Reference Freund and Antonsen2024), where the dashed line indicates unstable trajectories. The figure is meant to show the generic variation in the average axial velocity versus the axial field strength for a magneto-static wiggler, hence, it is not meant to correspond to the parameters used in the simulation. Note that the average transverse velocity $\beta _\perp ^2 =1-1/\gamma _b^2 - \beta _\parallel ^2$
, as the axial magnetic field increases (for given values of the wiggler period, field strength and electron energy) is illustrated in figure 7 (taken from Freund & Antonsen Reference Freund and Antonsen2024), where the dashed line indicates unstable trajectories. The figure is meant to show the generic variation in the average axial velocity versus the axial field strength for a magneto-static wiggler, hence, it is not meant to correspond to the parameters used in the simulation. Note that the average transverse velocity $\beta _\perp ^2 =1-1/\gamma _b^2 - \beta _\parallel ^2$![]() . Group I trajectories are generally found in the weak axial field regime below the magneto-resonance, $\varOmega _0 \leq \gamma _b k_w c$
. Group I trajectories are generally found in the weak axial field regime below the magneto-resonance, $\varOmega _0 \leq \gamma _b k_w c$![]() , where the Larmor period is longer than the wiggler period. Group II trajectories occur in the strong axial field regime where $\varOmega _0 \gg \gamma _b k_w c$
, where the Larmor period is longer than the wiggler period. Group II trajectories occur in the strong axial field regime where $\varOmega _0 \gg \gamma _b k_w c$![]() . We are most concerned with group II trajectories in which $\varOmega _0 \gg \gamma _b k_w c$
. We are most concerned with group II trajectories in which $\varOmega _0 \gg \gamma _b k_w c$![]() , which we expect to be relevant to the conditions in magnetar magnetospheres. As shown in figure 7, the axial velocity increases but asymptotes with increasing magnetic field in the group II regime, which implies that the FEL resonant wavelength decreases with increasing magnetic field but reaches a value that is relatively independent of the axial field strength.
, which we expect to be relevant to the conditions in magnetar magnetospheres. As shown in figure 7, the axial velocity increases but asymptotes with increasing magnetic field in the group II regime, which implies that the FEL resonant wavelength decreases with increasing magnetic field but reaches a value that is relatively independent of the axial field strength.

Figure 7. Illustration of the variation in the axial velocity with the axial magnetic field for group I and group II trajectories (Freund & Antonsen Reference Freund and Antonsen2024).
We remark that there are two possible interactions of an electron beam streaming along the field lines corresponding to the FEL resonance and that of a CARM. The ratio of the resonant frequencies of these two interaction mechanisms is given by
so that the FEL resonance is found at a lower frequency than that for the CARM for strong axial guide fields in the group II regime. For the parameters of interest here, the magneto-resonance is found for an axial field of approximately 0.10 kG as shown in figure 8. We are primarily concerned here with the strong axial field regime. This is a separate, and possibly astrophysically important emission mechanism. We leave the analysis of the CARM regime to a separate future investigation.

Figure 8. Plot showing the variation in $\varOmega _0/\gamma _b k_w c$![]() versus the axial field showing that group I orbits are found when $B_0 \le 0.10$
versus the axial field showing that group I orbits are found when $B_0 \le 0.10$![]() kG and group II orbits when $B_0 \ge 0.10$
kG and group II orbits when $B_0 \ge 0.10$![]() kG.
kG.
5 Conclusion
In this work we numerically study operation of the FEL in the astrophysically important guide-field dominated regime. In this regime particles mostly slide along the dominant guiding magnetic field and experience $\boldsymbol {E} \times \boldsymbol {B}$![]() drift in the field of the wiggler. Our parameters (energy of the beam, wavelength of the wiggler) closely match what is expected in the magnetospheres of neutron stars. The value of the guide field is, though, much smaller than expected. However, we verified that the wavelength becomes independent of the guide field (figure 4).
drift in the field of the wiggler. Our parameters (energy of the beam, wavelength of the wiggler) closely match what is expected in the magnetospheres of neutron stars. The value of the guide field is, though, much smaller than expected. However, we verified that the wavelength becomes independent of the guide field (figure 4).
Our results are encouraging. First, we see unseeded growth over fourteen orders of magnitude over the real physical scale of approximately a few kilometres. It is expected that the real magnetospheres are much ‘noisier’, with a mild level of intrinsically present turbulence. The presence of such turbulent Alfvén waves will provide seeds to jump start the operation of the FEL.
The most intriguing result is, perhaps, the fine spectral structure, figure 6, that qualitatively matches observations. Such a fine structure is an inherent property of SASE FEL, as different narrow modes are amplified parametrically.
Limitations of our approach include the following.
(i) One-dimensional approximation. In this case we neglect curvatures of the magnetic field lines and corresponding particles’ trajectories. We plan to address this in a separate work, using the MINERVA code.
(ii) The saturation level will be affected by the higher guiding field. For a single quasi-monochromatic wave, the ponderomotive potential (2.7) increases linearly with the EM wave intensity $E_w$
 , while the energy density of the EM waves increases quadratically ${\propto }E_w^2$
, while the energy density of the EM waves increases quadratically ${\propto }E_w^2$ . The balance is achieved at
(5.1)\begin{equation} \frac{E_{EM}}{E_{w}} = \frac{\omega_{p,b}^2}{ k_{w} c \varOmega_0}, \end{equation}where $\omega _{p,b}$
. The balance is achieved at
(5.1)\begin{equation} \frac{E_{EM}}{E_{w}} = \frac{\omega_{p,b}^2}{ k_{w} c \varOmega_0}, \end{equation}where $\omega _{p,b}$
 is the beam plasma density. This is an estimate of the saturation level of the EM waves in the beam frame.
is the beam plasma density. This is an estimate of the saturation level of the EM waves in the beam frame.(iii) We have not addressed the energy spread in the beam. It is expected that in the guide-field dominated regime the operation of the FEL is much more tolerant to the beam spread (Lyutikov Reference Lyutikov2021) since in this regime the particle trajectory is independent of energy. In the broadband case the saturation will be determined approximately by a (random phase) quasilinear diffusion. In this regime the growth rate of the EM energy of the wave due to the development of the parametric instability (2.8) will be balanced by the particle diffusion (random phases) in the turbulent EM field (the diffusion coefficient ${\propto }E_w^2$
 ).
).(iv) Coherence of the wiggler. We assumed a purely monochromatic wiggler. Spectral spread of the wiggler will tend to reduce the FEL efficiency.
We plan to address theses issues in a future publication.
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by NASA grant 80NSSC17K0757 and NSF grants 1903332 and 1908590.
Editor Luís O. Silva thanks the referees for their advice in evaluating this article.
Declaration of interests
The authors report no conflict of interest.