No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 10 December 2014
We describe a laboratory plasma physics experiment at Los Alamos National Laboratory that uses two merging supersonic plasma jets formed and launched by pulsed-power-driven railguns. The jets can be formed using any atomic species or mixture available in a compressed-gas bottle and have the following nominal initial parameters at the railgun nozzle exit: ne ≈ ni ~ 1016 cm−3, Te ≈ Ti ≈ 1.4 eV, Vjet ≈ 30–100 km/s, mean charge 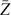 $\bar{Z}$ ≈ 1, sonic Mach number Ms ≡ Vjet/Cs > 10, jet diameter = 5 cm, and jet length ≈20 cm. Experiments to date have focused on the study of merging-jet dynamics and the shocks that form as a result of the interaction, in both collisional and collisionless regimes with respect to the inter-jet classical ion mean free path, and with and without an applied magnetic field. However, many other studies are also possible, as discussed in this paper.
$\bar{Z}$ ≈ 1, sonic Mach number Ms ≡ Vjet/Cs > 10, jet diameter = 5 cm, and jet length ≈20 cm. Experiments to date have focused on the study of merging-jet dynamics and the shocks that form as a result of the interaction, in both collisional and collisionless regimes with respect to the inter-jet classical ion mean free path, and with and without an applied magnetic field. However, many other studies are also possible, as discussed in this paper.