Article contents
Laminar and turbulent plasmoid ejection in a laboratory Parker Spiral current sheet
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 August 2021
Abstract
Quasi-periodic plasmoid formation at the tip of magnetic streamer structures is observed to occur in experiments on the Big Red Ball as well as in simulations of these experiments performed with the extended magnetohydrodynamics code, NIMROD. This plasmoid formation is found to occur on a characteristic time scale dependent on pressure gradients and magnetic curvature in both experiment and simulation. Single mode, or laminar, plasmoids exist when the pressure gradient is modest, but give way to turbulent plasmoid ejection when the system drive is higher, which produces plasmoids of many sizes. However, a critical pressure gradient is also observed, below which plasmoids are never formed. A simple heuristic model of this plasmoid formation process is presented and suggested to be a consequence of a dynamic loss of equilibrium in the high-$\beta$ region of the helmet streamer. This model is capable of explaining the periodicity of plasmoids observed in the experiment and simulations, and produces plasmoid periods of 90 minutes when applied to two-dimensional models of solar streamers with a height of $3R_\odot$
region of the helmet streamer. This model is capable of explaining the periodicity of plasmoids observed in the experiment and simulations, and produces plasmoid periods of 90 minutes when applied to two-dimensional models of solar streamers with a height of $3R_\odot$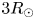 . This is consistent with the location and frequency at which periodic plasma blobs have been observed to form by Large Angle and Spectrometric Coronograph and Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation instruments.
. This is consistent with the location and frequency at which periodic plasma blobs have been observed to form by Large Angle and Spectrometric Coronograph and Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation instruments.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Author(s), 2021. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
REFERENCES
- 4
- Cited by



