Published online by Cambridge University Press: 26 June 2019
Wave dispersion in a pulsar plasma is discussed emphasizing the relevance of different inertial frames, notably the plasma rest frame 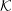 ${\mathcal{K}}$ and the pulsar frame
${\mathcal{K}}$ and the pulsar frame 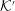 ${\mathcal{K}}^{\prime }$ in which the plasma is streaming with speed
${\mathcal{K}}^{\prime }$ in which the plasma is streaming with speed 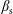 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}_{\text{s}}$. The effect of a Lorentz transformation on both subluminal,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}_{\text{s}}$. The effect of a Lorentz transformation on both subluminal, 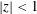 $|z|<1$, and superluminal,
$|z|<1$, and superluminal, 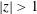 $|z|>1$, waves is discussed. It is argued that the preferred choice for a relativistically streaming distribution should be a Lorentz-transformed Jüttner distribution; such a distribution is compared with other choices including a relativistically streaming Gaussian distribution. A Lorentz transformation of the dielectric tensor is written down, and used to derive an explicit relation between the relativistic plasma dispersion functions in
$|z|>1$, waves is discussed. It is argued that the preferred choice for a relativistically streaming distribution should be a Lorentz-transformed Jüttner distribution; such a distribution is compared with other choices including a relativistically streaming Gaussian distribution. A Lorentz transformation of the dielectric tensor is written down, and used to derive an explicit relation between the relativistic plasma dispersion functions in 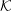 ${\mathcal{K}}$ and
${\mathcal{K}}$ and 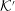 ${\mathcal{K}}^{\prime }$. It is shown that the dispersion equation can be written in an invariant form, implying a one-to-one correspondence between wave modes in any two inertial frames. Although there are only three modes in the plasma rest frame, it is possible for backward-propagating or negative-frequency solutions in
${\mathcal{K}}^{\prime }$. It is shown that the dispersion equation can be written in an invariant form, implying a one-to-one correspondence between wave modes in any two inertial frames. Although there are only three modes in the plasma rest frame, it is possible for backward-propagating or negative-frequency solutions in 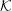 ${\mathcal{K}}$ to transform into additional forward-propagating, positive-frequency solutions in
${\mathcal{K}}$ to transform into additional forward-propagating, positive-frequency solutions in 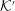 ${\mathcal{K}}^{\prime }$ that may be regarded as additional modes.
${\mathcal{K}}^{\prime }$ that may be regarded as additional modes.