Article contents
Closed maximality principles: implications, separations and combinations
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 12 March 2014
Abstract
I investigate versions of the Maximality Principles for the classes of forcings which are <κ-closed, <κ-directed-closed, or of the form Col(κ, <λ). These principles come in many variants, depending on the parameters which are allowed, I shall write MPΓ (A) for the maximality principle for forcings in Γ, with parameters from A. The main results of this paper are:
• The principles have many consequences, such as <κ-closed-generic 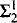 (Hκ) absoluteness, and imply, e.g., that ◊κ holds. I give an application to the automorphism tower problem, showing that there are Souslin trees which are able to realize any equivalence relation, and hence that there are groups whose automorphism tower is highly sensitive to forcing.
(Hκ) absoluteness, and imply, e.g., that ◊κ holds. I give an application to the automorphism tower problem, showing that there are Souslin trees which are able to realize any equivalence relation, and hence that there are groups whose automorphism tower is highly sensitive to forcing.
• The principles can be separated into a hierarchy which is strict, for many κ.
• Some of the principles can be combined, in the sense that they can hold at many different κ simultaneously.
The possibilities of combining the principles are limited, though: While it is consistent that MP<κ-closed(Hκ +) holds at all regular κ below any fixed α, the “global” maximality principle, stating that MP<κ-closed (Hκ ∪ {κ} ) holds at every regular κ, is inconsistent. In contrast to this, it is equiconsistent with ZFC that the maximality principle for directed-closed forcings without any parameters holds at every regular cardinal. It is also consistent that every local statement with parameters from Hκ⊦ that's provably <κ-closed-forceably necessary is true, for all regular κ.
Keywords
Information
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Association for Symbolic Logic 2008
References
REFERENCES
- 11
- Cited by

