Article contents
ZERO JORDAN PRODUCT DETERMINED BANACH ALGEBRAS
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 08 January 2020
Abstract
A Banach algebra 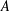 $A$ is said to be a zero Jordan product determined Banach algebra if, for every Banach space
$A$ is said to be a zero Jordan product determined Banach algebra if, for every Banach space 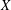 $X$, every bilinear map
$X$, every bilinear map 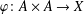 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}:A\times A\rightarrow X$ satisfying
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}:A\times A\rightarrow X$ satisfying 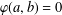 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(a,b)=0$ whenever
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(a,b)=0$ whenever  $a$,
$a$, 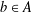 $b\in A$ are such that
$b\in A$ are such that 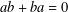 $ab+ba=0$, is of the form
$ab+ba=0$, is of the form 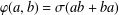 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(a,b)=\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}(ab+ba)$ for some continuous linear map
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(a,b)=\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}(ab+ba)$ for some continuous linear map  $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}$. We show that all
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}$. We show that all 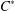 $C^{\ast }$-algebras and all group algebras
$C^{\ast }$-algebras and all group algebras 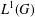 $L^{1}(G)$ of amenable locally compact groups have this property and also discuss some applications.
$L^{1}(G)$ of amenable locally compact groups have this property and also discuss some applications.
Keywords
MSC classification
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society , Volume 111 , Issue 2 , October 2021 , pp. 145 - 158
- Copyright
- © 2020 Australian Mathematical Publishing Association Inc.
Footnotes
Communicated by A. Sims
The authors were supported by MINECO grant PGC2018-093794-B-I00. The first, the third and the fourth named authors were supported by Junta de Andalucía grant FQM-185. The second named author was supported by ARRS grant P1-0288.
References
- 2
- Cited by



