Abha Arabic is a dialect of Arabic (ISO 693-3: ara), belonging to the Semitic language family group, and spoken primarily in Abha city. Abha Arabic can be broadly classified as a variety of Arabic from the Arabian Peninsula group (Versteegh, Reference Versteegh2014), and further sub-classified as a south (-west) Arabian dialect (Ingham, Reference Ingham1982). Abha city is the administrative capital of the province of Asir, in south-west Saudi Arabia (Figure 1). The population of Abha is approximately 290,185 and that of the Asir province is 1,601,725, according to the most recent data on the population (General Authority for Statistics, 2010). The province is named after the Asir tribe, who first inhabited Abha and the surrounding regions. The present day Abha Arabic dialect thus represents a blending of Bedouin and urban dialects. The first settlers to Abha were the Bani-Mghed tribe (an Asir tribe) followed by three additional Asir tribes (Alkam, Rabiah w Rufeda, Bani-Malik) and other nearby tribes such as the Gahtaːn, Bal-lahmir, Bal-lasmir, Shahran, Rejal Alma’, all of which had distinct dialects (Al-Azraqi, Reference Al-Azraqi1998). These dialects merged to varying degrees and were further influenced by urban education and mass media, which were and continue to be dominated by Modern Standard Arabic (henceforth MSA) (Al-Azraqi, Reference Al-Azraqi1998).Footnote 1

Figure 1. Map of Saudi Arabia showing Asir region with main cities.
As is the case with other Arabic dialects, Abha Arabic does not have its own writing system, and thus the alphabet of MSA is used instead in the relatively infrequent instances when Abha Arabic is written. Abha Arabic in written form is typically only used in chat applications between native speakers and sometimes in advertisements for added impact to attract people’s attention. Abha Arabic is primarily a spoken dialect which coexists with MSA in a situation of diglossia (Ferguson, Reference Ferguson1959). Abha Arabic is used in informal daily conversations, while MSA is used in formal situations such as in media, education, and formal meetings.
Like other Arabic dialects, Abha Arabic has received little attention in the literature; to our knowledge, there are only three studies devoted to this dialect. Al-Azraqi (Reference Al-Azraqi1998) focused on selected aspects of syntax while Nakshabandi (Reference Nakshabandi1988) focused on the phonology and morphology of Abha Arabic. However, although Nakshabandi’s phonological analysis included a description of the sounds, syllable structure, stress, and some phonological processes of the dialect, the phonetic description is not as detailed as those available for other Arabic dialects. In particular, an acoustic analysis is not conducted in Nakshabandi (Reference Nakshabandi1988). The third study of Abha Arabic, Al Malwi (Reference Al Malwi2017), provides some acoustic analyses but it focuses mainly on the effects of age and gender on the production of Voice Onset Time (VOT).
The present study thus aims to provide a comprehensive description of the main features of the phonological system of Abha Arabic. Audio data has been collected from participants who are native speakers of Abha Arabic between twenty-eight and forty-six years of age; the first author is also one of the participants. They all hold a university degree and speak Abha Arabic at home. The phonemic values of the sounds were identified by near/minimal pairs/sets. For the VOT, three males and three females uttered the words four times and only the first three repetitions were measured. For each vowel, five males and five females pronounced every word five times and only the first four tokens were measured to avoid including a final intonation contour. All samples were recorded in isolation. The data were analyzed using Praat (Boersma & Weenink, Reference Boersma and Weenink2021). The transcribed passage in the final section is a reading of ‘The North Wind and the Sun’ by the first author.
Consonants
Abha Arabic has twenty-seven consonants, while MSA has twenty-eight; this is due to the fact that /dˤ/ and /ðˤ/ merge into /ðˤ/ in Abha Arabic. A notable characteristic of Arabic is the existence of pharyngealized consonants, commonly known as emphatic consonants, which are represented by the symbol /ˤ/ in the IPA.

The following is a list of all the consonant phonemes in Abha Arabic. Details regarding any phonetic variation, when relevant, are included in the discussion that follows. Since Abha Arabic does not have a writing system, we use MSA orthography to write the words used in the list below.

Abha Arabic has seven plosives /b, t̪, d̪, t̪ˤ, k, ɡ, ʔ/ and, except for /ɡ/, they are all found in MSA. MSA voiceless uvular plosive /q/ corresponds to Abha Arabic voiced velar plosive /ɡ/. For example, MSA ![]() /ˈqaːla/ ‘he said’ and
/ˈqaːla/ ‘he said’ and ![]() /daˈqiːq/ ‘flour’ are /ɡaːl/ and /dɐˈɡiːɡ/ in Abha Arabic, respectively. /q/, however, appears in Abha Arabic as a phoneme with a limited application by younger speakers and educated people in formal situations, for instance /qalam/ ‘a pen’. Furthermore, the voiceless glottal stop /ʔ/ can appear word-initially, word-medially and word-finally in MSA and is pronounced [ʔ] in those contexts. However, in Abha Arabic, /ʔ/ only appears word-initially; it is /ʔ/ word-initially and /j/ word-medially if it follows /aː/, as in MSA
/daˈqiːq/ ‘flour’ are /ɡaːl/ and /dɐˈɡiːɡ/ in Abha Arabic, respectively. /q/, however, appears in Abha Arabic as a phoneme with a limited application by younger speakers and educated people in formal situations, for instance /qalam/ ‘a pen’. Furthermore, the voiceless glottal stop /ʔ/ can appear word-initially, word-medially and word-finally in MSA and is pronounced [ʔ] in those contexts. However, in Abha Arabic, /ʔ/ only appears word-initially; it is /ʔ/ word-initially and /j/ word-medially if it follows /aː/, as in MSA ![]() /ˈsaːʔɪl/ ‘liquid’, which is /ˈsaːjɪl/ in Abha Arabic. If /ʔ/ appears after a short vowel, it is deleted and the short vowel is lengthened. For instance, MSA
/ˈsaːʔɪl/ ‘liquid’, which is /ˈsaːjɪl/ in Abha Arabic. If /ʔ/ appears after a short vowel, it is deleted and the short vowel is lengthened. For instance, MSA ![]() /muʔmɪn/ ‘a believer’,
/muʔmɪn/ ‘a believer’, ![]() /ðiʔb/ ‘wolf’ and
/ðiʔb/ ‘wolf’ and ![]() /faʔs/ ‘axe’ are /ˈmuːmɪn/, /ðiːb/ and /faːs/ in Abha Arabic, respectively. /ʔ/ is also deleted word-finally, as in MSA
/faʔs/ ‘axe’ are /ˈmuːmɪn/, /ðiːb/ and /faːs/ in Abha Arabic, respectively. /ʔ/ is also deleted word-finally, as in MSA ![]() /ʕaˈʃaːʔ/ ‘dinner’, which is /ˈʕɐʃaː/ in Abha Arabic. These are common historical changes in Arabic dialects.
/ʕaˈʃaːʔ/ ‘dinner’, which is /ˈʕɐʃaː/ in Abha Arabic. These are common historical changes in Arabic dialects.
Voice Onset Time differentiates between three types of plosives in Abha Arabic (Table 1): (1) voiced plosives display voicing-lead, meaning that voicing starts before the burst; (2) voiceless plosives have long-lag VOT; and (3) the voiceless emphatic plosive /tˤ/ is pronounced with short-lag VOT (Figure 2) (Al Malwi, Reference Al Malwi2017). All possible vowels were used after a plosive since VOT is affected by the vowel height where VOT tends to be longer in high vowels than in low vowels (Morris, McCrea & Herring, Reference Morris, Mccrea and Herring2008). In careful pronunciation, the stop /t/ can be affricated, as in the example provided for /t/ in Table 1 /tiːn/ ‘figs’.
Table 1 Mean length (ms) of VOTs in Abha Arabic plosives. Each word was pronounced four times by three male and three female speakers of Abha Arabic. The first three tokens were measured (n = 770). Standard variations are reported in parentheses and number of tokens are reported in square brackets


Figure 2. Mean length and standard variation (ms) of VOT in Abha Arabic plosives word-initially. Values taken from 770 tokens produced by six Abha Arabic native speakers (three males and three females).
The voiced plosives /b/, /d/ and /ɡ/ undergo partial devoicing word-finally and are pronounced [b̥], [d̥] and [ɡ̥], respectively, while /t/ and /k/ are pronounced [th] and [kh] word-finally; an analysis of word-final voiced plosives using the fraction of locally unvoiced frames function on Praat shows devoicing of between 20% and 50% of the stop consonants from the beginning of closure up to the beginning of the burst. Therefore, the contrast between voiced and voiceless stops is mainly based on lack of aspiration or aspiration in word-final position. For example, ![]() /ʒɐdd/ is pronounced [ʒɐdt] ‘grandfather’ while
/ʒɐdd/ is pronounced [ʒɐdt] ‘grandfather’ while ![]() /ʒɐt/ is pronounced [ʒɐth] ‘she came’. Similarly,
/ʒɐt/ is pronounced [ʒɐth] ‘she came’. Similarly, ![]() /ʃɐɡɡ/ is pronounced [ʃɐɡk] ‘crack’ whereas
/ʃɐɡɡ/ is pronounced [ʃɐɡk] ‘crack’ whereas ![]() /ʃɐkk/ is pronounced [ʃɐkkh] ‘doubt’. The following four spectrograms illustrate the difference (Figures 3, 4, 5 and 6). Furthermore, the voiced plosives are devoiced if they appear in coda position before a final voiceless consonant (regressive assimilation). For instance,
/ʃɐkk/ is pronounced [ʃɐkkh] ‘doubt’. The following four spectrograms illustrate the difference (Figures 3, 4, 5 and 6). Furthermore, the voiced plosives are devoiced if they appear in coda position before a final voiceless consonant (regressive assimilation). For instance, ![]() /l-ˈsabt/ ‘Saturday’ is pronounced [ʔɐsˈsɐb̥t]. Another assimilation appears with the phoneme /n/. This consonant assimilates to the place of articulation of the following velar or labial consonants, for example,
/l-ˈsabt/ ‘Saturday’ is pronounced [ʔɐsˈsɐb̥t]. Another assimilation appears with the phoneme /n/. This consonant assimilates to the place of articulation of the following velar or labial consonants, for example, ![]() /ʒɐnb/ ‘side’ is pronounced [ʒɐmb̥] and
/ʒɐnb/ ‘side’ is pronounced [ʒɐmb̥] and  /mɪnk/ ‘from you M.SG.’ is pronounced [mɪŋkh].
/mɪnk/ ‘from you M.SG.’ is pronounced [mɪŋkh].

Figure 3. Partial devoicing of final /d/ in /ʒɐdd/ [ʒɐdt] ‘grandfather’.

Figure 4. Aspirated final /t/ in /ʒɐt/ [ʒɐth] ‘she came’.

Figure 5. Partial devoicing of final /ɡ/ in /ʃɐɡɡ/ [ʃɐɡk] ‘crack’.

Figure 6. Aspirated final /k/ in /ʃɐkk/ [ʃɐkkh] ‘doubt’.

Figure 7. A geminated /ʕ/ in /ˈnɐʕʕɐm/ ‘to soften the grind’ pronounced by a male Abha Arabic speaker.
Abha Arabic has one trill phoneme which is /r/. There is variation between speakers and /r/ can sometimes be pronounced as a fricative. Although the trill is the dominant, it can be pronounced as fricative when it’s proceeded or followed by a front vowel. For instance /riːʃ/ ‘feathers’ and /raːs/ ‘head’ are pronounced as fricative and trill respectively.
Abha Arabic has fourteen fricatives, which makes it the largest consonant group in this dialect of Arabic. While other varieties of Arabic maintain /dʒ/, such as MSA and San’ani Arabic (Watson, Reference Watson2002), MSA /dʒ/ corresponds to /ʒ/ in Abha Arabic as well as in Tihami Qahtani (Alqahtani, Reference Alqahtani2015). For example, the MSA word ![]() /dʒaˈmiːl/ ‘beautiful’ is /ʒɐˈmiːl/ in Abha Arabic. Pronouncing /dʒ/ as /ʒ/ is a salient feature of Syro-Lebanese/Syro-Palestinian dialects. Yet, the same process has been recorded in a few dialects outside of this area as well, like certain Gelet-speaking tribes in Iraq and Khuzestan (Bahrani & Ghavami, Reference Bahrani and Modarresi Ghavami2021).
/dʒaˈmiːl/ ‘beautiful’ is /ʒɐˈmiːl/ in Abha Arabic. Pronouncing /dʒ/ as /ʒ/ is a salient feature of Syro-Lebanese/Syro-Palestinian dialects. Yet, the same process has been recorded in a few dialects outside of this area as well, like certain Gelet-speaking tribes in Iraq and Khuzestan (Bahrani & Ghavami, Reference Bahrani and Modarresi Ghavami2021).
The consonant /ʕ/ shows the presence of continuous acoustic energy but no turbulent airflow, together with a high degree of constriction, “higher than is normally associated with strictures of open approximation” (Heselwood, Reference Heselwood2007, p. 9). Therefore, following (Heselwood, Reference Heselwood2007), Abha Arabic /ʕ/ could be described as a tight approximant as well (Figure 7).
While MSA has four pharyngealized consonant phonemes (/ðˤ/, /dˤ/, /tˤ/, and /sˤ/), Abha Arabic has three, since /ðˤ/ and /dˤ/ have merged into /ðˤ/. There is a similar tendency in many other Arabic dialects such as San’ani Arabic (Watson, Reference Watson2002), Damascus Syrian Arabic (Daher, Reference Daher1998), and Gulf Arabic (Hussain, Reference Hussain1985). The emphatic consonants /ðˤ/, /tˤ/ and /sˤ/ can trigger pharyngealization of neighbouring /r/ and /l/ in Abha Arabic. For instance, ![]() /sˤaːr/ ‘happened’ and
/sˤaːr/ ‘happened’ and ![]() /tˤaːl/ ‘he became tall’ are pronounced [sˤɑːrˤ] and [tˤɑːlˤ] in Abha Arabic, respectively. Furthermore, /l/ sometimes occurs as [lˤ] after a low vowel /ɐ/ and in specific lexical contexts, as in
/tˤaːl/ ‘he became tall’ are pronounced [sˤɑːrˤ] and [tˤɑːlˤ] in Abha Arabic, respectively. Furthermore, /l/ sometimes occurs as [lˤ] after a low vowel /ɐ/ and in specific lexical contexts, as in ![]() /ɐlˈlaːh/ [ʔɑlˁˈlˁɑːh] ‘God’.
/ɐlˈlaːh/ [ʔɑlˁˈlˁɑːh] ‘God’.
The lateral /l/ in the definite article /l-/ ‘the’ assimilates to the following consonant when it is followed by a coronal consonant; this process triggers gemination of the coronal consonant (Table 2). Some speakers, especially older speakers, however, use /ɪm-/ as the definite article instead of /l-/. If /ɪm-/ is used, no assimilation takes place. /ɪm-/ as the definite article has been observed in many dialects in southern Saudi Arabic such as Rejal Alma’ dialect (Asiri, Reference Asiri2009) and Tihami Qahtani (Alqahtani, Reference Alqahtani2015).
Table 2 Assimilation of /l-/ in the definite article

Vowels
Monophthongs

Abha Arabic has eight vowel phonemes: three short and five long: /iː/, /ɪ/, /eː/, /aː/, /ɐ/, /uː/, /ʊ/, /oː/. It should be noted that, although /aː/ is technically a low front vowel in the IPA (Cardinal Vowel 4), we are using this symbol to denote a low central vowel. MSA, in comparison, has three short and three long vowel phonemes: /iː/, /i/, /aː/, /a/, /uː/, /u/. Acoustic measurements for the F1 and F2 of each vowel phoneme in Abha Arabic after a non-emphatic consonant are included in Table 3. Vowel length is phonemic in Abha Arabic and the average length of each vowel in our samples is also included in Table 3; standard deviation is given in brackets. The words which have been analysed are those in Table 3. The vowels were measured in Praat (Boersma & Weenink, Reference Boersma and Weenink2021). Segmentation was performed manually and the measurements were taken using a script developed by the second author (Herrero de Haro, Reference Herrero de Haro2021). All settings were standard Praat (Boersma & Weenink, Reference Boersma and Weenink2021) except maximum formant, which was set at 5000 Hz for males, and 5500 Hz for females. The measurement taken for each vowel corresponds to the mean value of the first two formants from the middle 20% to 80% section of the vowel. Formant values have been normalised using the Nearey 1 formula (Nearey Terrance, Reference Nearey Terrance1977) and then scaled to Hz. The normalisation has been carried out using the NORM application (Thomas & Kendall, Reference Thomas and Kendall2007) (Table 3). F1 and F2 ellipses mark 1 standard deviation. The same process in terms of normalisation has been followed for vowels after an emphatic consonant (Table 4). For vowel plots, non-normalised mean formant values were used for vowels after a non-emphatic consonant (Figure 8) and vowels after an emphatic consonant (Figure 9).
Table 3 Mean F1 and F2 values (Hz) and duration of each vowel phoneme in Abha Arabic after /s/. Measurements obtained from a total of 320 tokens from ten speakers (five males and five females). Formant values normalised using the Nearey 1 formula and scaled to Hz. Standard deviation is given in brackets.


Figure 8. F1 and F2 mean values (Hz) for each vowel phoneme of Abha Arabic measured from the middle 20% to 80% section of each vowel after /s/. Measurements taken from 320 tokens from five male and five female Abha Arabic speakers. The ellipses show the F1 and F2 values to 1 standard deviation.

Figure 9. F1 and F2 mean values (Hz) for each vowel phoneme of Abha Arabic measured from the middle 20% to 80% section of each vowel after /sˤ/. Measurements taken from 320 tokens from five male and five female Abha Arabic speakers. The ellipses show the F1 and F2 values to 1 standard deviation.
Table 4 Mean F1 and F2 values (Hz) and duration of each vowel phoneme in Abha Arabic after /sˤ/. Measurements obtained from a total of 320 tokens from ten speakers (five males and five females). Formant values normalised using the Nearey 1 formula and scaled to Hz. Standard deviation is given in brackets.

The data from Table 3 and Figure 8 support transcribing the Abha Arabic vowels /iː/, /ɪ/, /eː/, /aː/, /ɐ/, /oː/, /uː/ and /ʊ/ as [iː], [ɪ], [eː], [aː], [ɐ], [oː], [uː] and [ʊ], respectively, in their phonetic realisation. As in other varieties of Arabic, the short vowels /i/, /a/ and /u/ are pronounced as lax when compared to their long counterparts, as it is the case in Gaza City Arabic (Cotter, 2022).
A comparison of the data in Table 3 with the data in Table 4 shows that, although F1 does not seem to change much in vowels depending on whether they precede a non-emphatic or an emphatic consonant, the situation is different for the F2. Vowels display a lower F2 when they are preceded by an emphatic consonant. This tendency seems to be larger in high front vowels and in low central vowels. Vowels seem to be slightly longer after an emphatic than after a non-emphatic consonant (Table 5).
Vowel length is phonemic in Abha Arabic and, as shown in Tables 3 and 4, long vowels have a duration which is over double that of short vowels. The long mid vowels /eː/ and /oː/ correspond to MSA diphthongs /aj/ and /aw/, respectively. For example, MSA ![]() /dʒajʃ/ ‘army’ and
/dʒajʃ/ ‘army’ and ![]() /θawb/ ‘dress’ are /ʒeːʃ/ and /θoːb/ in Abha Arabic, respectively. The emergence of the two long mid vowels is due to the coalescence of vowel-glide sequences, as has been reported in many Arabic dialects such as Cairene Arabic (Youssef, Reference Youssef2010) and Syrian Arabic (Almbark & Hellmuth, Reference Almbark and Hellmuth2015).
/θawb/ ‘dress’ are /ʒeːʃ/ and /θoːb/ in Abha Arabic, respectively. The emergence of the two long mid vowels is due to the coalescence of vowel-glide sequences, as has been reported in many Arabic dialects such as Cairene Arabic (Youssef, Reference Youssef2010) and Syrian Arabic (Almbark & Hellmuth, Reference Almbark and Hellmuth2015).
Abha Arabic low vowels /aː/ and /ɐ/ usually undergo lowering and backing to [ɑː] and [ɑ] in emphatic environments. For example ![]() /sˤaːm/ ‘he fasted’ and
/sˤaːm/ ‘he fasted’ and ![]() /sˤɐff/ ‘line’ are pronounced as [sˤɑːm] and [sˤɑff] in Abha Arabic. Furthermore, /r/ can trigger backing in /aː/ as /raːs/ ‘head’ is pronounced as [rɑːs].
/sˤɐff/ ‘line’ are pronounced as [sˤɑːm] and [sˤɑff] in Abha Arabic. Furthermore, /r/ can trigger backing in /aː/ as /raːs/ ‘head’ is pronounced as [rɑːs].
Closed syllable shortening is a process that occurs in Abha Arabic and in many Arabic dialects such as Cairene Arabic (Watson, Reference Watson2002), San’ani Arabic (Watson, Reference Watson2002), and Palestinian Arabic (Hall, Reference Hall2017). Closed syllable shortening happens when consonant-initial subject suffixes are added to the root of /CVːC/ verbs, as shown in Table 6.
Table 5 Differences between the normalised means of F1 and F2 values (Hz) of Abha Arabic vowels after /s/ and after /sˤ/. Measurements obtained from a total of 640 tokens from ten speakers (five males and five females). Formant values normalised using the Nearey 1 formula and scaled to Hz

Table 6 Closed syllable shortening in Abha Arabic

Table 7 Pronunciation of /aː/ in defective verbs

Defective verbs are subject to another type of vowel alteration. As explained in Nakshabandi (Reference Nakshabandi1988), when a consonant-initial subject suffix is connected to a defective verb that ends with /aː/, /aː/ surfaces as [eː]. However, when the verb is connected to a vowel-initial subject suffix, /aː/ is omitted (Table 7).
Prosodic features
Syllable structure
Syllable structure in Abha Arabic consists of onset, nucleus and coda. Utterance-initially, the onset is filled with [ʔ] if it is empty. The nucleus of a syllable is always either a short or a long vowel. The coda is optional and may comprise either one or two consonants. The observed syllable structures in Abha Arabic are included in Table 8.
Table 8 Abha Arabic Syllable Structure

Lexical stress
The placement of word stress is predictable based on syllable weight. Abha Arabic has three syllable weights: light (CV), heavy (CVː and CVC), and super-heavy (CVCC and CVːC). The placement of word stress in Abha Arabic seems to act similarly to other Arabic dialects such as Hijazi Arabic (Abaalkhail, Reference Abaalkhail1998) and Khuzestani Arabic (Bahrani & Ghavami, Reference Bahrani and Modarresi Ghavami2021). Word stress in Abha Arabic is governed by three rules:
-
(1) If the last syllable is superheavy, CVːC or CVCC, this last syllable carries the stress.

-
(2) If the last syllable is not superheavy, the stress falls on the penultimate syllable when the penultimate syllable is heavy, comprising of either CVː or CVC.

-
(3) If the last syllable is not superheavy and the penultimate syllable is not heavy, the stress falls on the antepenultimate syllable in polysyllabic words and on the penultimate in disyllabic words.

Different acoustic correlates were measured to quantify stress in Abha Arabic. These correlates include intensity, pitch, and duration. The following table shows the stress correlations in three words pronounced ten times each by a male Abha Arabic speaker. It appears that the duration is the most prominent parameter for stress (Table 9).
Table 9 Intensity, f0, and duration of the vowels in /kɐ.ˈtɐbt/ ‘I wrote’, /kɐ.tɐ.ˈbɐt.lɐ/ ‘she wrote for him’, and /ˈkɐ.tɐ.bɐt/ ‘she wrote’. Stressed vowels are marked in bold. Data were measured in ten repetitions of each word (thirty words resulted in ninety vowels) pronounced by a male Abha Arabic native speaker. Standard deviations are reported in parentheses.

Transcription
The transcriptions are based on a reading by the first author, a thirty-four-year-old male native speaker of Abha Arabic. The English version of ‘The North Wind and the Sun’ was translated into Abha Arabic by the first author. Even though Abha Arabic has no official writing system, the translation is written in Arabic script adapted to Abha Arabic.
The order of the presentation is:
-
Broad phonetic transcription
-
Orthographic version
-
Morphemic glossing
-
Translation

The North Wind and the Sun were disputing
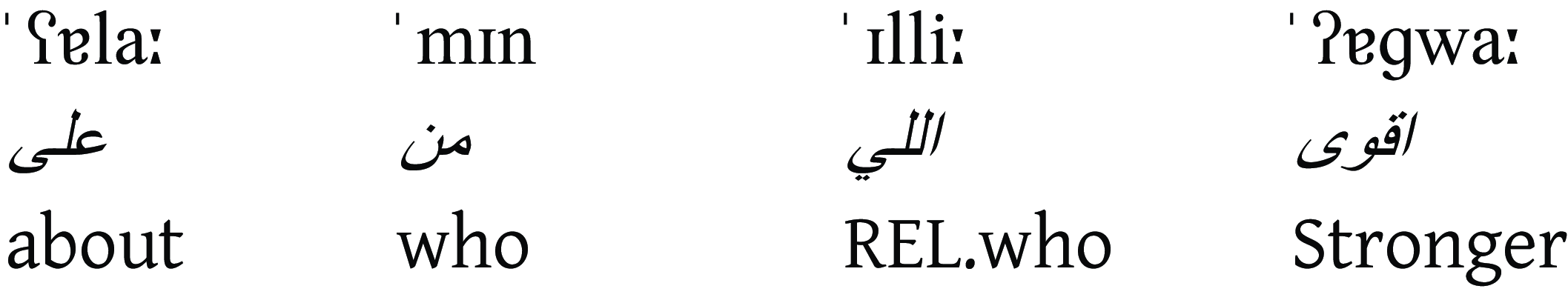
about who was the stronger

when a traveller came along wrapped in a warm cloak
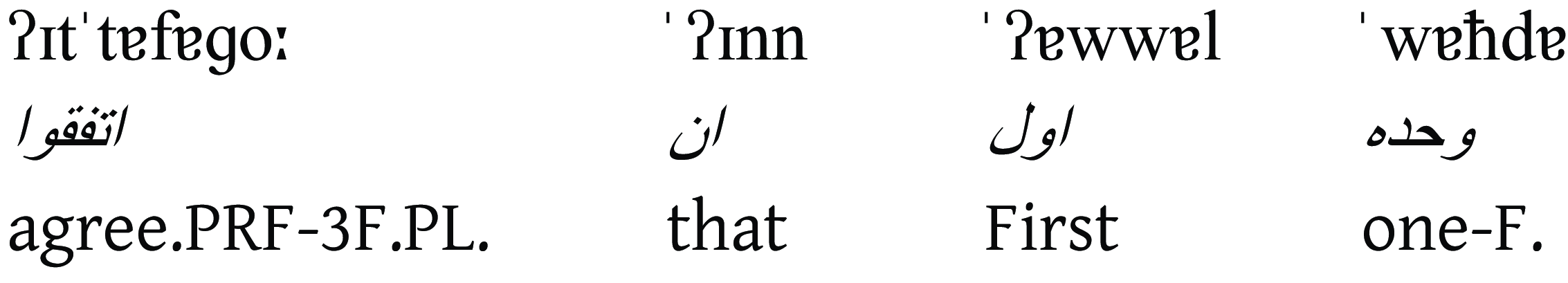
They agreed that the first one

succeeded in making the traveller take his cloak off

will be stronger than the other.

Then the North Wind blew as hard as it could,

but the more it blew

the more closely did the traveller fold his cloak around him
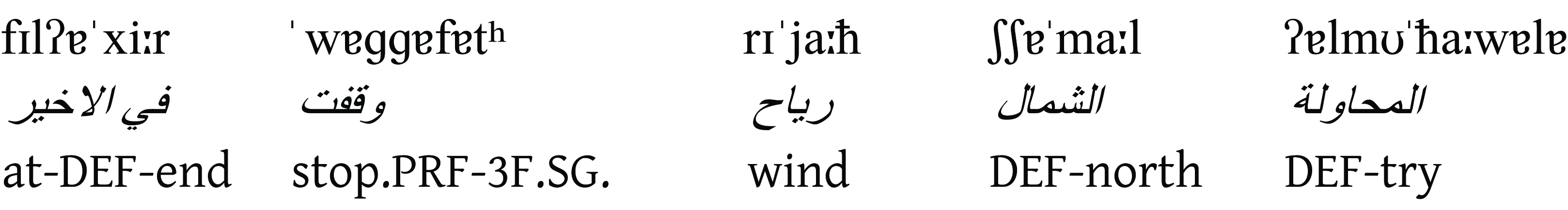
at last the North Wind gave up the attempt
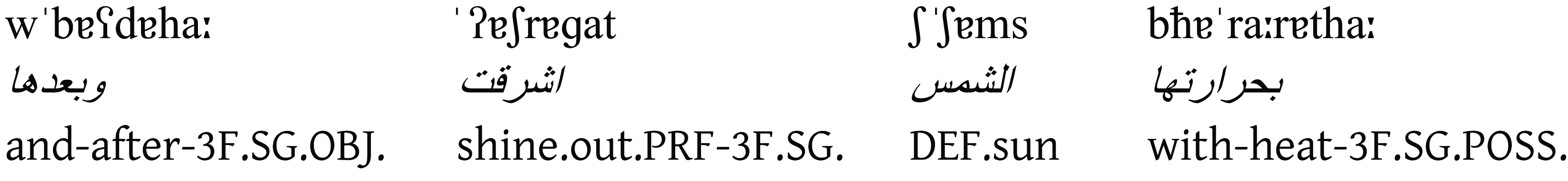
Then the Sun shined out warmly,
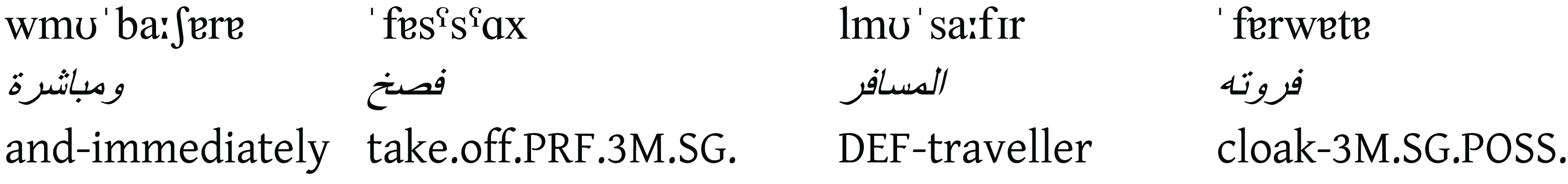
and immediately the traveller took off his cloak.

so the North Wind obliged to confess

that the Sun was the stronger.
Abbreviations
- 3
third person
- ADV
adverb
- DEF
definite
- F
feminine
- f0
fundamental frequency
- F1
1st formant
- F2
2nd formant
- IPM
imperative
- IPFV
imperfective
- M
masculine
- MSA
Modern Standard Arabic
- OBJ
Object
- PRF
perfect
- POSS
possessive
- PRN
pronoun
- PL
Plural
- REL
relative
- SG
singular
- VOT
voice onset time
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the participants for their participation in the study. We are also very grateful to the editors, audio manager, and the two anonymous reviewers of the Journal of the International Phonetic Association for their insightful comments and suggestions during the revision process of this illustration.
Supplementary material
To view supplementary material for this article, please visit https://doi.org/10.1017/S0025100323000269





















