Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Sharma, R. P.
and
Singh, Ram Kishor
2014.
Terahertz generation by two cross focused laser beams in collisional plasmas.
Physics of Plasmas,
Vol. 21,
Issue. 7,
Xia, Xiongping
2014.
Nonlinear structure of electromagnetic field, electron temperature and electron density in interaction of relativistic laser and plasma with density ripple.
Laser and Particle Beams,
Vol. 32,
Issue. 4,
p.
591.
Varshnety, Prateek
Sajal, Vivek
Chauhan, Prashant
Kumar, Ravindra
and
Sharma, Navneet K.
2014.
Effects of transverse static electric field on terahertz radiation generation by beating of two transversely modulated Gaussian laser beams in a plasma.
Laser and Particle Beams,
Vol. 32,
Issue. 3,
p.
375.
Varshney, Prateek
Sajal, Vivek
Baliyan, Sweta
Sharma, Navneet K.
Chauhan, Prashant K.
and
Kumar, Ravindra
2015.
Strong terahertz radiation generation by beating of two x-mode spatial triangular lasers in magnetized plasma.
Laser and Particle Beams,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 1,
p.
51.
Zhang, Xiao-Bo
Qiao, Xin
Cheng, Li-Hong
Tang, Rong-An
Zhang, Ai-Xia
and
Xue, Ju-Kui
2015.
Terahertz generation by beating two Langmuir waves in a warm and collisional plasma.
Physics of Plasmas,
Vol. 22,
Issue. 9,
Bakhtiari, Farhad
Yousefi, Masoud
Golmohammady, Shole
Jazayeri, Seyed Masoud
and
Ghafary, Bijan
2015.
Generation of terahertz radiation by beating of two circular flat-topped laser beams in collisional plasma.
Laser and Particle Beams,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 4,
p.
713.
Varshney, Prateek
Sajal, Vivek
Singh, Kunwar Pal
Kumar, Ravindra
and
Sharma, Navneet K.
2015.
Tunable and efficient terahertz radiation generation by photomixing of two super Gaussian laser pulses in a corrugated magnetized plasma.
Journal of Applied Physics,
Vol. 117,
Issue. 19,
Magesh Kumar, K. K.
Kumar, M.
Yuan, T.
Sheng, Z. M.
and
Chen, M.
2015.
Terahertz radiation from plasma filament generated by two-color laser gas–plasma interaction.
Laser and Particle Beams,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 3,
p.
473.
Bakhtiari, Farhad
Golmohammady, Shole
Yousefi, Masoud
Kashani, Fatemeh D.
and
Ghafary, Bijan
2015.
Generation of terahertz radiation in collisional plasma by beating of two dark hollow laser beams.
Laser and Particle Beams,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 3,
p.
463.
Bakhtiari, Farhad
Golmohammady, Shole
Yousefi, Masoud
and
Ghafary, Bijan
2016.
Terahertz radiation generation and shape control by interaction of array Gaussian laser beams with plasma.
Physics of Plasmas,
Vol. 23,
Issue. 12,
Hematizadeh, Ayoob
Bakhtiari, Farhad
Jazayeri, Seyed Masud
and
Ghafary, Bijan
2016.
Strong terahertz radiation generation by beating of two spatial-triangular beams in collisional magnetized plasma.
Physics of Plasmas,
Vol. 23,
Issue. 5,
Hematizadeh, A.
Jazayeri, S.M.
and
Ghafary, B.
2016.
Generation of terahertz radiation by beating of two laser beams in collisional magnetized plasma.
Laser and Particle Beams,
Vol. 34,
Issue. 4,
p.
569.
Verma, N.K.
and
Jha, P.
2016.
Enhanced terahertz radiation generation by two-color laser pulses propagating in plasma.
Laser and Particle Beams,
Vol. 34,
Issue. 2,
p.
378.
Hematizadeh, Ayoob
and
Jazayeri, Seyed Masud
2017.
Study of Terahertz Radiation Generation by Two Laser Beams in an Axial Magnetized Rippled Density Plasma.
IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science,
Vol. 45,
Issue. 7,
p.
1717.
Sepehri Javan, N.
and
Rouhi Erdi, F.
2017.
Theoretical study of the generation of terahertz radiation by the interaction of two laser beams with graphite nanoparticles.
Journal of Applied Physics,
Vol. 122,
Issue. 22,
Mann, K.L.
Sajal, V.
and
Sharma, N.K.
2017.
Excitation of terahertz radiation generation by obliquely incident beating lasers on a hot magnetized plasma with step density profile.
Laser and Particle Beams,
Vol. 35,
Issue. 3,
p.
528.
Varshney, P.
Sajal, V.
Upadhyay, A.
Chakera, J. A.
and
Kumar, R.
2017.
Tunable terahertz radiation generation by nonlinear photomixing of cosh-Gaussian laser pulses in corrugated magnetized plasma.
Laser and Particle Beams,
Vol. 35,
Issue. 2,
p.
279.
Bakhtiari, Farhad
Esmaeilzadeh, Mahdi
and
Ghafary, Bijan
2017.
Terahertz radiation with high power and high efficiency in a magnetized plasma.
Physics of Plasmas,
Vol. 24,
Issue. 7,
Mann, Kusum Lata
Sajal, Vivek
Varshney, Prateek
and
Sharma, Navneet K.
2017.
Terahertz radiation generation by pulse slippage of Cosh-Gaussian lasers in a corrugated magnetized plasma.
Physics of Plasmas,
Vol. 24,
Issue. 12,
Varshney, Prateek
Upadhayay, Ajit
Madhubabu, K.
Sajal, Vivek
and
Chakera, J. A.
2018.
Strong terahertz radiation generation by cosh-Gaussian laser beams in axially magnetized collisional plasma under non-relativistic ponderomotive regime.
Laser and Particle Beams,
Vol. 36,
Issue. 2,
p.
236.
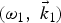 $\lpar {\rm \omega}_1\comma \; \vec k_1 \rpar $ and
$\lpar {\rm \omega}_1\comma \; \vec k_1 \rpar $ and 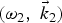 $\lpar {\rm \omega}_2\comma \; \vec k_2 \rpar $, respectively in a magnetized plasma. Terahertz wave is resonantly excited at frequency
$\lpar {\rm \omega}_2\comma \; \vec k_2 \rpar $, respectively in a magnetized plasma. Terahertz wave is resonantly excited at frequency 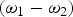 $\lpar {\rm \omega}_1 - {\rm \omega}_2 \rpar $ and wave number (k1 − k2 + q) with a wave number mismatch factor q which is introduced by the periodicity of plasma density ripples. In this process, the lasers exert a beat ponderomotive force on plasma electrons and impart them an oscillatory velocity with both transverse and longitudinal components in the presence of transverse static magnetic field. The oscillatory velocity couples with density ripples and produces a nonlinear current that resonantly excites the terahertz radiation. Effects of periodicity of density ripples and applied magnetic field are analyzed for strong THz radiation generation. The terahertz radiation generation efficiency is found to be directly proportional to the square of density ripple amplitude and rises with the magnetic field strength. With the optimization of these parameters, the efficiency ~10−3 is achieved in the present scheme. The frequency and power of generated THz radiation can be better tuned with the help of parameters like density ripple amplitude, periodicity and applied magnetic field strength in the present scheme.
$\lpar {\rm \omega}_1 - {\rm \omega}_2 \rpar $ and wave number (k1 − k2 + q) with a wave number mismatch factor q which is introduced by the periodicity of plasma density ripples. In this process, the lasers exert a beat ponderomotive force on plasma electrons and impart them an oscillatory velocity with both transverse and longitudinal components in the presence of transverse static magnetic field. The oscillatory velocity couples with density ripples and produces a nonlinear current that resonantly excites the terahertz radiation. Effects of periodicity of density ripples and applied magnetic field are analyzed for strong THz radiation generation. The terahertz radiation generation efficiency is found to be directly proportional to the square of density ripple amplitude and rises with the magnetic field strength. With the optimization of these parameters, the efficiency ~10−3 is achieved in the present scheme. The frequency and power of generated THz radiation can be better tuned with the help of parameters like density ripple amplitude, periodicity and applied magnetic field strength in the present scheme.
