Article contents
Parametric excitation of surface plasma waves over a metallic surface by laser in an external magnetic field
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 February 2018
Abstract
Effects of external static magnetic field (applied in 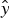 $\hat y$-direction) on resonant excitation of surface plasma waves (SPW) have been investigated over the metal free space interface. The high power laser
$\hat y$-direction) on resonant excitation of surface plasma waves (SPW) have been investigated over the metal free space interface. The high power laser  $({\rm \omega} _0,\;\vec k_{0z})$ is incident over the metal surface and exerts a ponderomotive force on the metal electrons in the skin layer. The ponderomotive force disturbs the quasi-neutrality of plasma which results into the excitation of space charge field at the frequency 2ω0. The electron density perturbation at frequency 2ω0 driven by self-consistent space charge potential couples with the oscillatory velocity due to the seed SPW
$({\rm \omega} _0,\;\vec k_{0z})$ is incident over the metal surface and exerts a ponderomotive force on the metal electrons in the skin layer. The ponderomotive force disturbs the quasi-neutrality of plasma which results into the excitation of space charge field at the frequency 2ω0. The electron density perturbation at frequency 2ω0 driven by self-consistent space charge potential couples with the oscillatory velocity due to the seed SPW 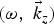 $({\rm \omega}, \;\vec k_z)$ and produces nonlinear current to drive another counter propagating SPW
$({\rm \omega}, \;\vec k_z)$ and produces nonlinear current to drive another counter propagating SPW 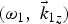 $({\rm \omega} _1,\;\vec k_{1z})$ at the phase matching conditions of frequency ω = ω1 − 2ω0 and wavenumber
$({\rm \omega} _1,\;\vec k_{1z})$ at the phase matching conditions of frequency ω = ω1 − 2ω0 and wavenumber 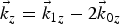 $\vec k_z = \vec k_{1z} - 2\vec k{}_{0z}$ (by feedback mechanism). The parametric process becomes resonant at 2ω0 ≈ ωp and the maximum growth rate is achieved for an incidence angle of laser θ = 40°. The growth rate of the process reduces to half on increasing the magnetic field from 0.49 to 2.45 MG. The present study may be significant to the laser absorption experiments where surface rippling can strongly affect the laser energy absorption.
$\vec k_z = \vec k_{1z} - 2\vec k{}_{0z}$ (by feedback mechanism). The parametric process becomes resonant at 2ω0 ≈ ωp and the maximum growth rate is achieved for an incidence angle of laser θ = 40°. The growth rate of the process reduces to half on increasing the magnetic field from 0.49 to 2.45 MG. The present study may be significant to the laser absorption experiments where surface rippling can strongly affect the laser energy absorption.
Information
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Cambridge University Press 2018
References
- 1
- Cited by

