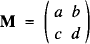Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by Crossref.
Hunziker, Markus
Machiavelo, António
and
Park, Jihun
2004.
Chebyshev polynomials over finite fields and reversibility of σ-automata on square grids.
Theoretical Computer Science,
Vol. 320,
Issue. 2-3,
p.
465.
Raghavan, V.
Veeravalli, V.V.
and
Sayeed, A.M.
2008.
Quantized Multimode Precoding in Spatially Correlated Multiantenna Channels.
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing,
Vol. 56,
Issue. 12,
p.
6017.
Li, Yue-Xian
Lukeman, Ryan
and
Edelstein-Keshet, Leah
2008.
Minimal mechanisms for school formation in self-propelled particles.
Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena,
Vol. 237,
Issue. 5,
p.
699.
Zhang, Zhongzhi
Zhou, Shuigeng
Qi, Yi
and
Guan, Jihong
2008.
Topologies and Laplacian spectra of a deterministic uniform recursive tree.
The European Physical Journal B,
Vol. 63,
Issue. 4,
p.
507.
Sirianunpiboon, Songsri
Calderbank, A. Robert
and
Howard, Stephen D.
2008.
Bayesian Analysis of Interference Cancellation for Alamouti Multiplexing.
IEEE Transactions on Information Theory,
Vol. 54,
Issue. 10,
p.
4755.
Barrière, L.
Comellas, F.
Dalfó, C.
and
Fiol, M.A.
2008.
On the spectra of hypertrees.
Linear Algebra and its Applications,
Vol. 428,
Issue. 7,
p.
1499.
Zhang, Zhongzhi
Qi, Yi
Zhou, Shuigeng
Lin, Yuan
and
Guan, Jihong
2009.
Recursive solutions for Laplacian spectra and eigenvectors of a class of growing treelike networks.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 80,
Issue. 1,
Ezra, Gregory S
and
Wiggins, Stephen
2009.
Impenetrable barriers in phase space for deterministic thermostats.
Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical,
Vol. 42,
Issue. 4,
p.
042001.
Barrière, L.
Comellas, F.
Dalfó, C.
and
Fiol, M.A.
2009.
The hierarchical product of graphs.
Discrete Applied Mathematics,
Vol. 157,
Issue. 1,
p.
36.
Carli, Ruggero
and
Bullo, Francesco
2009.
Quantized Coordination Algorithms for Rendezvous and Deployment.
SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization,
Vol. 48,
Issue. 3,
p.
1251.
Barrière, L.
Dalfó, C.
Fiol, M.A.
and
Mitjana, M.
2009.
The generalized hierarchical product of graphs.
Discrete Mathematics,
Vol. 309,
Issue. 12,
p.
3871.
Qi, Yi
Zhang, Zhongzhi
Ding, Bailu
Zhou, Shuigeng
and
Guan, Jihong
2009.
Structural and spectral properties of a family of deterministic recursive trees: rigorous solutions.
Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical,
Vol. 42,
Issue. 16,
p.
165103.
Lukeman, Ryan
Li, Yue-Xian
and
Edelstein-Keshet, Leah
2009.
A Conceptual Model for Milling Formations in Biological Aggregates.
Bulletin of Mathematical Biology,
Vol. 71,
Issue. 2,
p.
352.
Barrière, L.
Comellas, F.
Dalfó, C.
and
Fiol, M.A.
2009.
On the hierarchical product of graphs and the generalized binomial tree.
Linear and Multilinear Algebra,
Vol. 57,
Issue. 7,
p.
695.
Kazemitabar, J.
and
Jafarkhani, H.
2009.
Performance analysis of multiple antenna multi-user detection.
p.
150.
Woelki, Marko
and
Mallick, Kirone
2010.
Transfer matrices for the totally asymmetric simple exclusion process.
Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical,
Vol. 43,
Issue. 18,
p.
185003.
Carli, Ruggero
Bullo, Francesco
and
Zampieri, Sandro
2010.
Quantized average consensus via dynamic coding/decoding schemes.
International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control,
Vol. 20,
Issue. 2,
p.
156.
Choi, Eun-Mi
2010.
RESULTANT AND DISCRIMINANT OF ITERATE POLYNOMIALS.
Honam Mathematical Journal,
Vol. 32,
Issue. 3,
p.
493.
Collins, Peter
Ezra, Gregory S.
and
Wiggins, Stephen
2010.
Phase space structure and dynamics for the Hamiltonian isokinetic thermostat.
The Journal of Chemical Physics,
Vol. 133,
Issue. 1,
Zhang, Zhongzhi
Qi, Yi
Zhou, Shuigeng
Gao, Shuyang
and
Guan, Jihong
2010.
Explicit determination of mean first-passage time for random walks on deterministic uniform recursive trees.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 81,
Issue. 1,